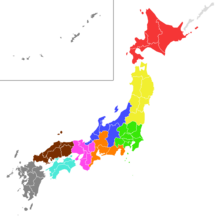
List of regions of Japan
They are widely used in, for example, maps, geography textbooks, and weather reports, and many businesses and institutions use their home regions in their names as well, for example Kyushu National Museum, Kinki Nippon Railway, Chūgoku Bank, and Tōhoku University.
This is a list of Japan's major islands, traditional regions, and subregions, going from northeast to southwest.
Examples of regional divisions of Japan as used by various institutions are: In the later stages of World War II, in preparation for an Allied invation of the home islands, regions served as administrative units between the Home Ministry and the governments of prefectures from 1943.
In 1945, they were consolidated into eight centralized "regional governorates-general" (地方総監府, chihō sōkan-fu) with authority of command over the subordinate prefectural governments.
The regions corresponded territorially to the military districts (軍管区, gunkan-ku) as used by the Imperial Army in 1945.