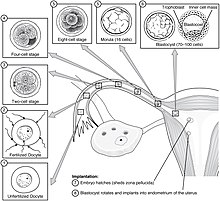
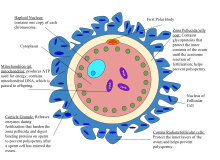
Human fertilization
[1] The result of this union leads to the production of a fertilized egg called a zygote, initiating embryonic development.
[3][4] Upon encountering the secondary oocyte, the acrosome of the sperm produces enzymes which allow it to burrow through the outer shell called the zona pellucida of the egg.
[7] Sperm cells were discovered in 1677 by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, who believed that Aristotle had been proven correct.
[10] Progesterone binds to the CatSper receptor on the sperm membrane and increases intracellular calcium levels, causing hyperactive motility.
[15] After binding to the corona radiata the sperm reaches the zona pellucida, which is an extracellular matrix of glycoproteins.
As a population, mature haploid sperm cells have on average 50% genome similarity, so the premature acrosomal reactions aid fertilization by a member of the same cohort.
When the sperm enters the perivitelline space, a sperm-specific protein Izumo on the head binds to Juno receptors on the oocyte membrane.
After approximately 40 minutes, the other Juno receptors on the oocyte are lost from the membrane, causing it to no longer be fusogenic.
Additionally, the cortical reaction will happen which is caused by ovastacin binding and cleaving ZP2 receptors on the zona pellucida.
The pronuclei migrate toward the center of the oocyte, rapidly replicating their DNA as they do so to prepare the zygote for its first mitotic division.
Upon subsequently undergoing mitosis (which includes pulling of chromatids towards centrioles in anaphase) the cell gathers genetic material from the male and female together.
[citation needed] Fertilization is the event most commonly used to mark the beginning point of life, in descriptions of prenatal development of the embryo or fetus.
Gestational age, in contrast, takes the beginning of the last menstrual period (LMP) as the start point.
For example, it is a better predictor than postnatal age for risk of intraventricular hemorrhage in premature babies treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Whether that results in the process of contact between the sperm and egg, or the state of health of the biological parent carrying the zygote cell.