Business process management
[1] As an approach, BPM sees processes as important assets of an organization that must be understood, managed, and developed to announce and deliver value-added products and services to clients or customers.
[citation needed] Although BPM initially focused on the automation of business processes with the use of information technology, it has since been extended[by whom?]
Also, the coupling of BPM to industry methodologies allows users to continually streamline and optimize the process to ensure that it is tuned to its market need.
[18][full citation needed] As of 2012[update] research on BPM has paid increasing attention to the compliance of business processes.
[citation needed] Business process management activities can be arbitrarily grouped into categories such as design, modeling, execution, monitoring, and optimization.
Areas of focus include representation of the process flow, the factors within it, alerts and notifications, escalations, standard operating procedures, service level agreements, and task hand-over mechanisms.
The proposed improvement could be in human-to-human, human-to-system or system-to-system workflows, and might target regulatory, market, or competitive challenges faced by the businesses.
Modeling takes the theoretical design and introduces combinations of variables (e.g., changes in rent or materials costs, which determine how the process might operate under different circumstances).
BPM software suites such as BPMS or iBPMS or low-code platforms are positioned at the business process layer.
However, automating a process definition requires flexible and comprehensive infrastructure, which typically rules out implementing these systems in a legacy IT environment.
Predictive Business Process Monitoring concerns the application of data mining, machine learning, and other forecasting techniques to predict what is going to happen with running instances of a business process, allowing to make forecasts of future cycle time, compliance issues, etc.
Techniques for predictive business process monitoring include Support Vector Machines,[25] Deep Learning approaches, and Random Forest.
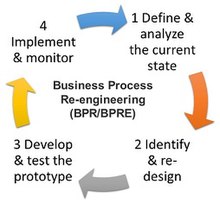
BPR aims to help organizations fundamentally rethink how they do their work in order to improve customer service, cut operational costs, and become world-class competitors.
[27] BPR seeks to help companies radically restructure their organizations by focusing on the ground-up design of their business processes.
RAD enables businesses to deploy applications more quickly and more cost effectively, while also offering improved change and version management.
Currently, the international standards for the task have limited BPM to the application in the IT sector, and ISO/IEC 15944 covers the operational aspects of the business.
[30] Other standards are currently being worked upon to assist in BPM implementation (BPMN, enterprise architecture, Business Motivation Model).
BPM is now considered a critical component of operational intelligence (OI) solutions to deliver real-time, actionable information.
OI solutions use real-time information to take automated action based on pre-defined rules so that security measures and or exception management processes can be initiated.
Cloud computing business process management is the use of (BPM) tools that are delivered as software services (SaaS) over a network.
The benefits of using cloud BPM services include removing the need and cost of maintaining specialized technical skill sets in-house and reducing distractions from an enterprise's main focus.
The emerging Internet of things poses a significant challenge to control and manage the flow of information through large numbers of devices.
To cope with this, a new direction known as BPM Everywhere shows promise as a way of blending traditional process techniques, with additional capabilities to automate the handling of all the independent devices.