Hybrid electric vehicle
The presence of the electric powertrain, which has inherently better energy conversion efficiency, is intended to achieve either better fuel economy or better acceleration performance than a conventional vehicle.
Worldwide increases in the price of petroleum caused many automakers to release hybrids in the late 2000s; they are now perceived as a core segment of the automotive market of the future.
[25][26] The twelfth generation of the Corolla line-up was launched in Brazil in September 2019, which included an Altis trim with the first version of a flex-fuel hybrid powered by a 1.8-litre Atkinson engine.
[28] To take advantage of the emission reduction potential of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), appropriate design of their energy management systems (EMSs) to control the power flow between the engine and the battery is essential.
A prototype was built in 1889, an experimental tram car was run in Pullman, Illinois, in 1891, and a production locomotive was sold to a street railway company in Cedar Falls, Iowa, in 1897.
In 1900, while employed at Lohner Coach Factory, Ferdinand Porsche developed the Mixte,[3][36] a 4WD series-hybrid version of "System Lohner–Porsche" electric carriage that previously appeared in 1900 Paris World Fair.
[citation needed] During the Second World War, Ferdinand Porsche sought to use his firm's experience in hybrid drivetrain design for powering armored fighting vehicles for Nazi Germany.
A series of designs, starting with the VK 3001 (P), the unsuccessful VK 4501 (P) heavy tank prototype (which became the Elefant tank destroyer) and concluding with the heaviest armored fighting vehicle ever prototyped, the Panzerkampfwagen Maus of nearly 190 tonnes in weight, were just two examples of a number of planned Wehrmacht "weapons systems" (including the highly-"electrified" subsystems on the Fw 191 bomber project), crippled in their development by the then-substandard supplies of electrical-grade copper, required for the electric final drives on Porsche's armored fighting vehicle powertrain designs.
The scheme proposed by Fiat is defined as "parallel hybrid": the petrol engine is connected to the differential with a 1:1 direct gear ratio, without gearbox, instead of the clutch there was an 8-inch torque converter followed by the transmission shaft on which the rotor of the electric motor is keyed, the latter powered by a 12-batteries pack.
The regenerative brake concept was further developed in the early 1980s by David Arthurs, an electrical engineer, using off-the shelf components, military surplus, and an Opel GT.
The design was realistic and already mass production-oriented, with minimal modifications to the standard body and a weight increase of only 150 kg (110 for the batteries, 20 for the electric engine and 10 for power electronics).
[55] The United States National Research Council (USNRC) cited automakers' moves to produce HEVs as evidence that technologies developed under PNGV were being rapidly adopted on production lines, as called for under Goal 2.
Based on information received from automakers, NRC reviewers questioned whether the "Big Three" would be able to move from the concept phase to cost effective, pre-production prototype vehicles by 2004, as set out in Goal 3.
The redesigned 2004 Toyota Prius (second generation) improved passenger room, cargo area, and power output, while increasing energy efficiency and reducing emissions.
[58] The Hyundai Elantra LPI Hybrid was unveiled at the 2009 Seoul Motor Show, and sales began in the South Korean domestic market in July 2009.
The 2016 model year Prius Eco surpassed the 2000 first generation Honda Insight as the all-time EPA-rated most fuel efficient gasoline-powered car available in the U.S. without plug-in capability.
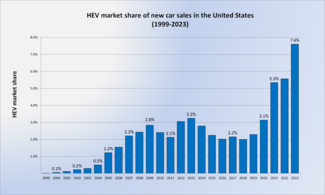
[10] The hybrid market share of new car sales began to increase significantly in 2009, when the government implemented aggressive fiscal incentives for fuel efficient vehicles and the third generation Prius was introduced.
Despite keeping to the top-selling spot, total Prius sales for 2011 were 20% lower than 2010 due partly to the disruptions caused by the March 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, and also because government incentives for hybrid cars were scaled back.
[citation needed] FedEx, along with Eaton Corp. in the US and Iveco in Europe, has begun deploying a small fleet of Hybrid diesel electric delivery trucks.
[253][254] In some cases, manufacturers are producing HEVs that use the added energy provided by the hybrid systems to give vehicles a power boost, rather than significantly improved fuel efficiency compared to their traditional counterparts.
In the future, manufacturers may provide HEV owners with the ability to partially control this balance (fuel efficiency vs. added performance) as they wish, through a user-controlled setting.
The ability to mass-produce these items helps to overcome the investment hurdles faced by start-up brands and bring new engineering concepts into mainstream markets.
In 2000, North America's first hybrid electric taxi was put into service in Vancouver, British Columbia, operating a 2001 Toyota Prius which traveled over 332,000 km (206,000 mi) before being retired.
In 2003, GM introduced a hybrid diesel-electric military (light) truck, equipped with a diesel electric and a fuel cell auxiliary power unit.
In May 2003, JR East started test runs with the so-called NE (new energy) train and validated the system's functionality (series hybrid with lithium-ion battery) in cold regions.
[306] Diesel-electric locomotives may not always be considered HEVs, not having energy storage on board, unless they are fed with electricity via a collector for short distances (for example, in tunnels with emission limits), in which case they are better classified as dual-mode vehicles.
The most advanced are the Zunum Aero 10-seater, the Airbus E-Fan X demonstrator, the VoltAero Cassio, the UTC modified Bombardier Dash 8, and the Ampaire Electric EEL.
Residents of Ontario and Quebec in Canada can claim a rebate on the Provincial Retail Sales Tax of up to Can$2,000 on the purchase or lease of a hybrid electric vehicle.
In 2009 the Japanese government implemented a set of policies and incentives that included a scrappage program, tax breaks on hybrid vehicles and other low emission cars and trucks, and a higher levy on gasoline that raised prices in the order of US$4.50 per gallon.
[325] Drivers of HEVs in the United Kingdom benefit from the lowest band of vehicle excise duty (car tax), which is based on carbon dioxide emissions.