IMAX
The single-projector/single-camera system they eventually settled upon was designed and built by Shaw based upon a novel "Rolling Loop" film-transport technology purchased from Peter Ronald Wright Jones, a machine shop worker from Brisbane, Australia.
As it became clear that a single, large-screen image had more impact than multiple smaller ones and was a more viable product direction, Multiscreen changed its name to IMAX.
[7] IMAX Chief Administration Officer Mary Ruby was quoted as saying, "Although many people may think 'IMAX' is an acronym, it is, in fact, a made-up word.
[26] The Wall Street Journal revealed that the new cameras will be made out of carbon fiber and titanium, and they will feature a five inch color display along with wireless capability.
IMAX film is shipped to theaters in several small reels that are spliced into one continuous length that is then wound into a platter, a process that may take hours to complete.
By the early 1990s, a separate DTS-based 6-track digital sound system was used, similarly locked to the projector by a SMPTE time code synchronization apparatus, the audio played off a series of proprietarily encoded CD-ROM discs.
[39] IMAX projectors are pin-stabilized; this means that four registration pins engage the perforations at the corners of the projected frame to ensure perfect alignment.
[46] In July 2008, the company introduced a digital projection system, which it has not given a distinct name or brand, designed for multiplex theatres with screens no wider than 21.3 m (70 ft).
IDF initially used 2K-resolution Christie xenon projectors, with a Texas Instruments Digital Light Processing (DLP) engine, but in 2012 IMAX announced that they would be switching to Barco as their primary supplier.
[citation needed] Also, the rows of seats are set at a steep angle (up to 30° in some domed theatres) so that the audience is facing the screen directly.
Several of the early films that had been produced in digital 3D for release in conventional theaters were also presented in IMAX 3D, including Avatar, Gravity and The Amazing Spider-Man.
[79] Higher production costs, and the high "wear-and-tear" on the prints and projectors, doomed the IMAX HD system, but, not before many theatres had been retrofitted to project at 48 frames, especially in Canada, in order to play Momentum.
IMAX cameras have been used while orbiting the Earth, climbing Mount Everest, exploring the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean, and visiting the Antarctic.
Cyberworld even presented open-matte 3D versions of the bar sequence from Antz and the "Homer3" segment from The Simpsons; both coincidentally were animated at Pacific Data Images.
With the unveiling of the DMR process (see below), Warner Bros. Pictures especially embraced the format beginning in 2003 with the two Matrix sequels, Reloaded and Revolutions.
Since The Prisoner of Azkaban in 2004, Warner Bros. began releasing the Harry Potter film franchise in IMAX to strong financial success.
[citation needed] Success for Warner Bros. and IMAX followed in later years with I Am Legend, Happy Feet, Batman Begins and The Dark Knight.
Reviewers have generally praised the results of the DMR blowup process, which are visually and audibly superior to the same films projected in 35mm.
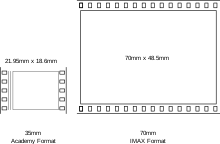
[citation needed] But some filmmakers, such as producer Frank Marshall, point out that DMR blowups are not comparable to films created directly in the 70 mm 15 perf IMAX format, and that directors Ron Howard and George Lucas expected better.
[98] They note that the decline of Cinerama coincided roughly with its replacement by a simpler, cheaper, technically inferior version, and view DMR with alarm.
A year later, director Michael Bay was inspired by IMAX's use in The Dark Knight to feature big-screen sequences in Transformers: Revenge of the Fallen.
[111] He also added that the IMAX format offered the viewer more immersion than digital 3D due to its brighter, higher quality image, which is projected on a larger screen, without the need for specialised glasses.
Ghost Protocol opened on December 16, 2011, in almost 500 IMAX venues worldwide a week before its wide release where it earned third place in the box office and $12 million.
On July 9, 2014, Bad Robot (J. J. Abrams's production company) confirmed via a picture uploaded to Twitter that one sequence in Disney and Lucasfilm's Star Wars: The Force Awakens would be captured with the IMAX 15/70 perf film camera, in addition to the standard 35 mm film cameras that Abrams and his cinematographer Dan Mindel have employed for shooting the movie.
[117] The next installment in the franchise Rian Johnson's Star Wars: The Last Jedi, released in December 2017, also included sequences shot with 15/70mm IMAX cameras.
[119] Other films between 2016 and 2021 that captured with IMAX cameras were Zack Snyder's Batman v Superman: Dawn of Justice, Clint Eastwood's Sully, Damien Chazelle's First Man, Jon Favreau's The Lion King, Patty Jenkins' Wonder Woman 1984 and Cary Joji Fukunaga's No Time to Die.
The large format company is also consulting with leading cinematographers including Linus Sandgren (No Time to Die), Rachel Morrison (Black Panther), Bradford Young (Arrival), Dan Mindel (Star Trek) and Nolan's go-to DP, Hoyte van Hoytema.
Later he recommend "So for the 30 or so minutes of the movie in IMAX, we shot with those lenses opened up to the 1.43 aspect ratio and composed for that while keeping the composition as clear and as solid for a 2.39 crop from the center.
[132] The award cited IMAX's innovations in creating and developing a method of filming and exhibiting large-format, wide-angle motion pictures.
[citation needed] The Science Museum London and BFI IMAX Cinema have also hosted computer game tournaments using digital projectors.