IT disaster recovery
DR employs policies, tools, and procedures with a focus on IT systems supporting critical business functions.
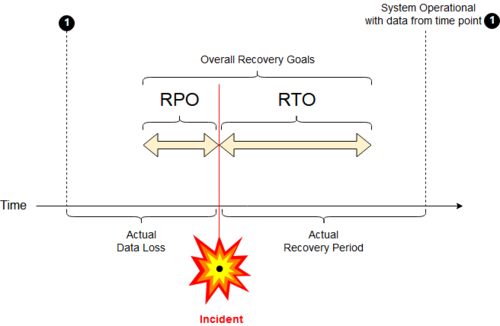
IT service continuity (ITSC) is a subset of BCP,[4] which relies on the metrics (frequently used as key risk indicators) of recovery point/time objectives.
This was withdrawn following the publication in March 2011 of ISO/IEC 27301, "Security techniques — Guidelines for information and communication technology readiness for business continuity.
[9] The business continuity group conducts timed rehearsals (or actuals), during which RTA gets determined and refined as needed.
[9] A Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the maximum acceptable interval during which transactional data is lost from an IT service.
[13] A recovery that is not instantaneous restores transactional data over some interval without incurring significant risks or losses.
RTO and the RPO must be balanced, taking business risk into account, along with other system design criteria.
An offsite mainframe could be loaded from backup tapes pending recovery of the primary site; downtime was relatively less critical.
[20][21] During the 1980s and 90s, computing grew exponentially, including internal corporate timesharing, online data entry and real-time processing.
Regulatory agencies became involved; availability objectives of 2, 3, 4 or 5 nines (99.999%) were often mandated, and high-availability solutions for hot-site facilities were sought.
Preparedness measures for all categories and types of disasters fall into the five mission areas of prevention, protection, mitigation, response, and recovery.
[24] 2015 disaster recovery statistics suggest that downtime lasting for one hour can cost[25][failed verification] As IT systems have become increasingly critical to the smooth operation of a company, and arguably the economy as a whole, the importance of ensuring the continued operation of those systems, and their rapid recovery, has increased.
Common strategies include: Precautionary strategies may include: Disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) is an arrangement with a third party vendor to perform some or all DR functions for scenarios such as power outages, equipment failures, cyber attacks, and natural disasters.