Indole alkaloid
An infusion of Calabar bean seeds was given to people accused of crime in Nigeria: its rejection by stomach was regarded as a sign of innocence, otherwise, the person was killed via the action of physostigmine, which is present in the plant and which causes paralysis of the heart and lungs.
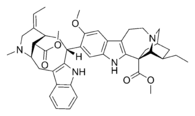
The latter include terpenoid structural elements, synthesized by living organisms from dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and/or isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP):[8] There are also purely structural classifications based on the presence of carbazole, β-carboline or other units in the carbon skeleton of the alkaloid molecule.
Simple (non-isoprenoid) β-carboline derivatives include harmine, harmaline, harmane[17] and a slightly more complex structure of canthinone.
The simplest such amide is ergine, and more complex can be distinguished into the following groups:[26][27] Ergotinine, discovered in 1875, and ergotoxine (1906) were subsequently proven to be a mixture of several alkaloids.
In pure form, the first ergot alkaloids, ergotamine and its isomer ergotaminine were isolated by Arthur Stoll in 1918.
[27] Most monoterpenoid alkaloids include a 9 or 10 carbon fragment (bold in image) (originating from the secologanin), and the configuration allows grouping to Corynanthe, Iboga and Aspidosperma classes.
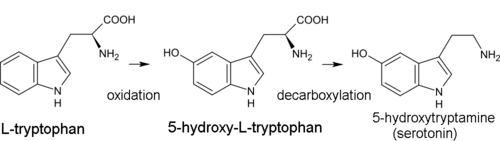
[33] The plants that are rich in non-isoprenoid indole alkaloids include harmal (Peganum harmala), which contains harmane, harmine and harmaline, and Calabar bean (Physostigma venenosum) containing physostigmine.
[35] Despite the considerable structural diversity, most of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids is localized in three families of dicotyledon plants: Apocynaceae (genera Alstonia, Aspidosperma, Rauvolfia and Catharanthus), Rubiaceae (Corynanthe) and Loganiaceae (Strychnos).
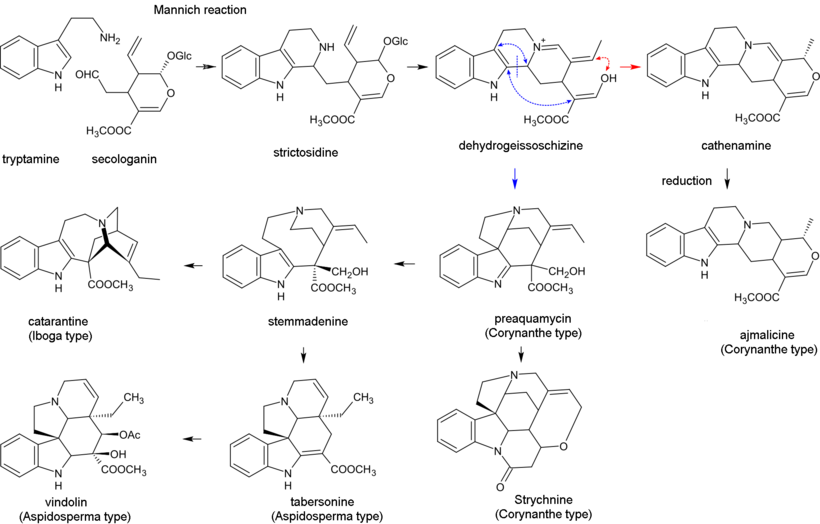
[13] Biosynthesis of β-carboline alkaloids occurs through the formation of Schiff base from tryptamine and aldehyde (or keto acid) and subsequent intramolecular Mannich reaction, where the C(2) carbon atom of indole serves as a nucleophile.
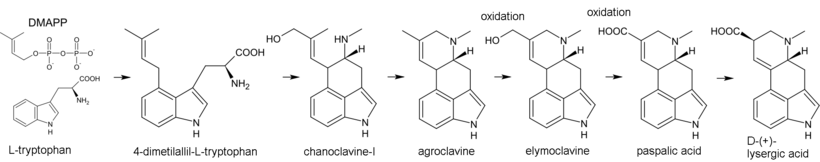
[42] Biosynthesis of ergot alkaloids begins with the alkylation of tryptophan by dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), where the carbon atom C(4) in the indole nucleus plays the role of the nucleophile.
[43] Biosynthesis of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids begins with the Mannich reaction of tryptamine and secologanin; it yields strictosidine which is converted to 4,21-dehydrogeissoschizine.
Then, the biosynthesis of most alkaloids containing the unperturbed monoterpenoid part (Corynanthe type) proceeds through cyclization with the formation of cathenamine and subsequent reduction to ajmalicine in the presence of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).
[50][51] So ergotamine is a partial agonist of α-adrenergic and 5-HT2 receptors, and thus narrows blood vessels and stimulates constriction of the uterus.
[55][56] Yohimbine is more selective to α2 adrenoceptor;[56] by blocking presynaptic α2-adrenoceptors, it increases the release of norepinephrine thereby raising the blood pressure.
[58] Reserpine reduces concentration of monoamines in presynaptic and synaptic neurons, thereby inducing antihypertensive and antipsychotic effects.
Rauvolfia serpentina, which contains reserpine as the active substance, was used for over 3000 years in India to treat snake bites and insanity.
Reserpine was the second (after chlorpromazine) antipsychotic drug; however, it showed relatively weak action and strong side effects, and is not used for this purpose any longer.
[55] Physostigmine – an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase – and its synthetic analogs are used in the treatment of glaucoma, Alzheimer's disease (rivastigmine) and myasthenia (neostigmine, pyridostigmine, distigmine).
Medical use of ibogaine is hindered by its legal status, as it is banned in many countries as a powerful psychedelic drug with dangerous implications of overdose.
The Aztecs used and the Mazatec people continue to use psilocybin mushrooms and the psychoactive seeds of morning glory species like Ipomoea tricolor.
[73] Psychotria viridis contains the psychedelic drug DMT, while Banisteriopsis caapi contains harmala alkaloids, which act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
[74] The venom of the Colorado River toad, Bufo alvarius, may have used as a psychedelic drug, its active constituents being 5-MeO-DMT and bufotenin.