Solar System
There is a strong consensus among astronomers[e] that the Solar System has at least nine dwarf planets: Ceres, Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, Makemake, Gonggong, Eris, and Sedna.
[14] As is typical of molecular clouds, this one consisted mostly of hydrogen, with some helium, and small amounts of heavier elements fused by previous generations of stars.
[14] As the contracting nebula spun faster, it began to flatten into a protoplanetary disc with a diameter of roughly 200 AU[14][16] and a hot, dense protostar at the center.
[20][21] Due to their higher boiling points, only metals and silicates could exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun (within the frost line).
[23] Following the dissipation of the protoplanetary disk, the Nice model proposes that gravitational encounters between planetisimals and the gas giants caused each to migrate into different orbits.
During this period, the grand tack hypothesis suggests that a final inward migration of Jupiter dispersed much of the asteroid belt, leading to the Late Heavy Bombardment of the inner planets.
[26][27] The Solar System remains in a relatively stable, slowly evolving state by following isolated, gravitationally bound orbits around the Sun.
At that time, the core of the Sun will contract with hydrogen fusion occurring along a shell surrounding the inert helium, and the energy output will be greater than at present.
[44] The boundary in the Solar System beyond which those volatile substances could coalesce is known as the frost line, and it lies at roughly five times the Earth's distance from the Sun.
[56][57] The planets, dominated by Jupiter, account for most of the rest of the angular momentum due to the combination of their mass, orbit, and distance from the Sun, with a possibly significant contribution from comets.
Attempts have been made to determine a relationship between these orbital distances, like the Titius–Bode law[60] and Johannes Kepler's model based on the Platonic solids,[61] but ongoing discoveries have invalidated these hypotheses.
The density of cosmic rays in the interstellar medium and the strength of the Sun's magnetic field change on very long timescales, so the level of cosmic-ray penetration in the Solar System varies, though by how much is unknown.
It has a higher abundance of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ("metals" in astronomical parlance) than the older population II stars in the galactic bulge and halo.
[84] Activity on the Sun's surface, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, disturbs the heliosphere, creating space weather and causing geomagnetic storms.
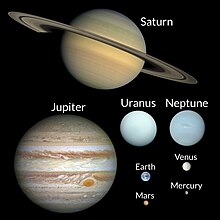
[89] Composed mainly of silicates and metals,[90] the objects of the inner Solar System are relatively close to the Sun; the radius of this entire region is less than the distance between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn.
Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth, and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface features, such as rift valleys and volcanoes.
[91] Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of carbonaceous, refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice.
[91] Jupiter and Saturn are composed mainly of gases with extremely low melting points, such as hydrogen, helium, and neon,[166] hence their designation as gas giants.
[167] Uranus and Neptune are ice giants,[168] meaning they are largely composed of 'ice' in the astronomical sense (chemical compounds with melting points of up to a few hundred kelvins[166] such as water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide.
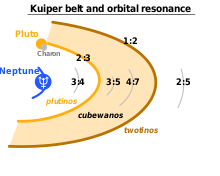
These are former Kuiper belt and scattered disc objects (SDOs) that were gravitationally perturbed closer to the Sun by the outer planets, and are expected to become comets or be ejected out of the Solar System.
[199] Members of the classical Kuiper belt are sometimes called "cubewanos", after the first of their kind to be discovered, originally designated 1992 QB1, (and has since been named Albion); they are still in near primordial, low-eccentricity orbits.
When a comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a coma: a long tail of gas and dust often visible to the naked eye.
Oort cloud objects move very slowly, and can be perturbed by infrequent events, such as collisions, the gravitational effects of a passing star, or the galactic tide, the tidal force exerted by the Milky Way.
[257] The Sun's Hill sphere with respect to the galactic nucleus, the effective range of its gravitational influence, is thought to extend up to a thousand times farther and encompasses the hypothetical Oort cloud.
[263] The Local Bubble is a small superbubble compared to the neighboring wider Radcliffe Wave and Split linear structures (formerly Gould Belt), each of which are some thousands of light-years in length.
[277] If it orbited close to the center, gravitational tugs from nearby stars could perturb bodies in the Oort cloud and send many comets into the inner Solar System, producing collisions with potentially catastrophic implications for life on Earth.
[277] However, according to the controversial Shiva hypothesis, the changing position of the Solar System relative to other parts of the Milky Way could explain periodic extinction events on Earth.
Up to the Late Middle Ages–Renaissance, astronomers from Europe to India believed Earth to be stationary at the center of the universe[280] and categorically different from the divine or ethereal objects that moved through the sky.
Using a heliocentric model that improved upon Copernicus by allowing orbits to be elliptical, and the precise observational data of Tycho Brahe, Kepler produced the Rudolphine Tables, which enabled accurate computations of the positions of the then-known planets.
[292] In 1838, Friedrich Bessel successfully measured a stellar parallax, an apparent shift in the position of a star created by Earth's motion around the Sun, providing the first direct, experimental proof of heliocentrism.