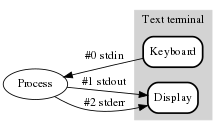
Stream (computing)
In computer science, a stream is a sequence of potentially unlimited data elements made available over time.
A stream can be thought of as items on a conveyor belt being processed one at a time rather than in large batches.
Normal functions cannot operate on streams as a whole because they have potentially unlimited data.
The term "stream" is also applied to file system forks, where multiple sets of data are associated with a single filename.
Here "stream" is used to indicate "variable size data", as opposed to fixed size metadata such as extended attributes, but differs from "stream" as used otherwise, meaning "data available over time, potentially infinite".