International relations since 1989
[1] This period has also seen the expansion of communications with mobile phones and the Internet, which have caused fundamental societal changes in business, politics, and how individuals networked along common interests and sought information.
[4] Predominant factors and trends included the continued mass mobilization of capital markets through neoliberalism, the thawing and sudden end of the Cold War after four decades of fear, the beginning of the widespread proliferation of new media such as the Internet and email, and increasing skepticism towards government.
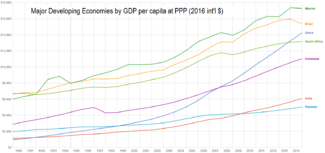
The rapid catching-up of emerging economies with developed countries sparked some protectionist tensions during the period and was partly responsible for an increase in energy and food prices at the end of the decade.
E-mail continued to be popular throughout the decade and began to replace paper-based "snail mail" as the primary way of sending letters and other messages to people in distant locations.
It solidified its position as an emerging superpower despite conflicts caused by its territorial claims and internal security policies in Hong Kong, Xinjiang, and Tibet.
U.S. forces killed Osama bin Laden and The rise of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant extremist organization in 2014 erased the Syria-Iraq border, resulting in a multinational intervention against it.
Online nonprofit organisation WikiLeaks gained international attention for publishing classified information on topics including Guantánamo Bay, Syria, the Afghan and Iraq wars, and United States diplomacy.
It led to postponement or cancellation of sporting, religious, political and cultural events, widespread supply shortages, leading to panic buying, and decreased emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases.
[21] During the presidency of Donald Trump, U.S. foreign policy was noted for its unpredictability and reneging on prior international commitments,[22][23][24][25] upending diplomatic conventions, embracing political and economic brinkmanship with most adversaries, and straining relations with traditional allies.
[26][27][22] As president, Trump described himself as a nationalist[28] while espousing isolationist, non-interventionist, and protectionist views;[29][30][31][32] he personally praised some populist, neo-nationalist, illiberal, and authoritarian governments, while antagonizing others, as administration diplomats nominally continued to pursue pro-democracy ideals abroad.
[33] The presidency of Joe Biden emphasizes repairing US alliances, which had been damaged under the Trump administration,[34][35] and returning the U.S. to a "position of trusted leadership" among world democracies to counter challenges from Russia and China.
[46] AUKUS will enable the three countries to share information in areas including artificial intelligence, cyber, underwater systems and long-range strike capabilities.
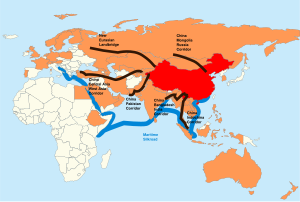
In early 1992, Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping made a series of political pronouncements designed to give new impetus to and reinvigorate the process of economic reform.
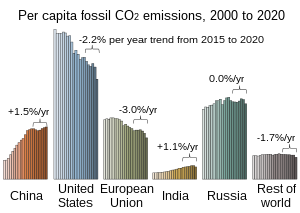
Global warming is driven largely by the emissions of greenhouse gases due to human economic activity, especially the burning of fossil fuels, certain industries like cement and steel production, and land use for agriculture and forestry.
[74] Americans who had been optimistic about the emergence of democratic characteristics in response to the rapid economic growth in China were stunned and disappointed by the brutal crackdown of the pro-democratic Tiananmen Square protests in 1989.
[77][78] Relations with the new Biden administration in 2021 included heightened tensions over trade, technology and human rights, particularly regarding Hong Kong, and the treatment of minorities in China.
There were no disasters but Russian athletes were again embarrassed by a doping scandal, the media coverage was eclipsed by rising war fears in Europe regarding Russia and Ukraine, and growing anxiety about the future of the sporting movement, according to Steven Lee Myers and Kevin Draper.
Of the 91 countries participating, Norway and Germany dominated the medal count, followed by the Russian athletes who played regardless of Russia itself being banned for a major doping scandal.
Orville Schell, an American expert on China, stated: "Such an august occasion, designed to promote openness, good sportsmanship and transnational solidarity, ended up being a heavily policed, brittle, Potemkin-like simulacrum of the Olympic ideal.
The US mortgage-backed securities, which had risks that were hard to assess, were marketed around the world and a broad-based credit boom fed a global speculative bubble in real estate and equities.
At the same time, the regional economies of Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore and South Korea experienced high growth rates, of 8–12% GDP, in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
As the crisis spread, most of Southeast Asia and Japan saw slumping currencies, devalued stock markets and other asset prices, and a precipitous rise in private debt.
[95] The International Monetary Fund (IMF) stepped in to initiate a $40 billion program to stabilize the currencies of South Korea, Thailand, and Indonesia, economies particularly hard hit by the crisis.
After 30 years in power, Indonesian President Suharto was forced to step down on May 21, 1998, in the wake of widespread rioting that followed sharp price increases caused by a drastic devaluation of the rupiah.
Only Singapore and Taiwan proved relatively insulated from the shock, but both suffered serious hits in passing, the former due to its size and geographical location between Malaysia and Indonesia.
[96] Following the end of the Cold War, the European Economic Community pushed for closer integration, co-operation in foreign and home affairs, and started to increase its membership into the neutral and former communist countries.
(Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, which had been part of the Soviet Union; Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia, five former-communist countries; Malta, and the divided island of Cyprus.)
Beginning in 2014, Ukraine has been in a state of revolution and unrest with two breakaway regions (Donetsk and Lugansk) attempting to join Russia as full federal subjects.
Many countries of this region joined the European Union, namely Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia.
The invasion caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II, with more than 6.4 million Ukrainians fleeing the country and a third of the population displaced.