Jones diagram
In a Jones diagram opposite directions of an axis represent different quantities, unlike in a Cartesian graph where they represent positive or negative signs of the same quantity.
A common application of Jones diagrams is in photography, specifically in displaying sensitivity to light with what are also called "tone reproduction diagrams".
These diagrams are used in the design of photographic systems (film, paper, etc.)
The Jones diagram concept can be used for variables that depend successively on each other.
Jones's original diagram used eleven quadrants[how?]
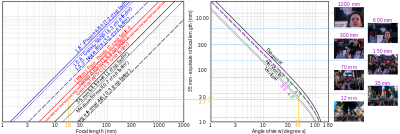

"a graphical illustration of a Jones Diagram for calibrating user specified tone reproduction curve (TRC)"