Kan fibration
Kan fibrations are the fibrations of the standard model category structure on simplicial sets and are therefore of fundamental importance.
Kan complexes are the fibrant objects in this model category.
, is the representable simplicial set Applying the geometric realization functor to this simplicial set gives a space homeomorphic to the topological standard
, corresponding to the boundary of the n-simplex, with the k-th face removed.
This may be formally defined in various ways, as for instance the union of the images of the n maps
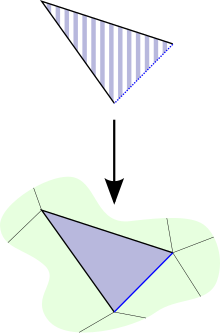
look like the black V at the top of the adjacent image.
is a simplicial set, then maps correspond to collections of
Stated this way, the definition is very similar to that of fibrations in topology (see also homotopy lifting property), whence the name "fibration".
(a consequence of the Yoneda lemma), this definition can be written in terms of simplices.
Since the black V in the lower diagram is filled in by the blue
-simplex, if the black V above maps down to it then the striped blue
, the one-point simplicial set, is a Kan fibration.
Conversely, every Kan complex has this property, hence it gives a simple technical condition for a Kan complex.
, Taking the set of these maps for all non-negative
, any continuous function defined on these faces can be extended to
In particular, for a simplicial abelian group, its geometric realization is homotopy equivalent to a product of Eilenberg-Maclane spaces
are correspond to Kan complexes of some simplicial set.
In fact, this set can be constructed explicitly using the Dold–Kan correspondence of a chain complex and taking the underlying simplicial set of the simplicial abelian group.
Another important source of examples are the simplicial sets associated to a small groupoid
This is defined as the geometric realization of the simplicial set
gives a counter example since it cannot be extended to a map
but this isn't a map of simplicial sets.
there is an associated simplicial set called the function complex
(since the first factor of Hom is contravariant) defined by sending a map
This complex has the following exponential law of simplicial sets
is in the function complex in the category of simplicial sets) induced from the commutative diagram
The homotopy groups of a fibrant simplicial set may be defined combinatorially, using horns, in a way that agrees with the homotopy groups of the topological space which realizes it.
of simplicial sets fitting into a certain commutative diagram:
is mapped to a point is equivalent to the definition of the sphere
Defining the group structure requires a little more work.