KeeLoq
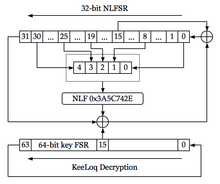
KeeLoq is a proprietary hardware-dedicated block cipher that uses a non-linear feedback shift register (NLFSR).
KeeLoq has been used in many remote keyless entry systems by such companies like Chrysler,[2] Daewoo, Fiat, Ford,[3] GM, Honda, Mercedes-Benz,[3] Toyota, Volvo, Volkswagen Group, Clifford, Shurlok, and Jaguar.
A 32-bit initialization vector is linearly added (XORed) to the 32 least significant bits of the key prior to encryption and after decryption.
KeeLoq cipher accepts 64-bit keys and encrypts 32-bit blocks by executing its single-bit NLFSR for 528 rounds.
[7] A detailed description of an inexpensive prototype device designed and built by Samy Kamkar to exploit this technique appeared in 2015.
[citation needed] In 2007, researchers in the COSIC group at the university at Leuven, Belgium, (K.U.Leuven) in cooperation with colleagues from Israel found a new attack against the system.
[12] In March 2008, researchers from the Chair for Embedded Security of Ruhr University Bochum, Germany, presented a complete break of remote keyless entry systems based on the KeeLoq RFID technology.
The attack by the Bochum team allows recovering the secret cryptographic keys embedded in both the receiver and the remote control.