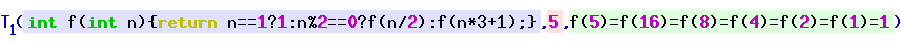Kleene's T predicate
In computability theory, the T predicate, first studied by mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene, is a particular set of triples of natural numbers that is used to represent computable functions within formal theories of arithmetic.
Informally, the T predicate tells whether a particular computer program will halt when run with a particular input, and the corresponding U function is used to obtain the results of the computation if the program does halt.
As with the smn theorem, the original notation used by Kleene has become standard terminology for the concept.
[1] The definition depends on a suitable Gödel numbering that assigns natural numbers to computable functions (given as Turing machines).
This numbering must be sufficiently effective that, given an index of a computable function and an input to the function, it is possible to effectively simulate the computation of the function on that input.
predicate is obtained by formalizing this simulation.
takes three natural numbers as arguments.
encodes a computation history of the computable function with index
, and the program halts as the last step of this computation history.
That is, If all three of these questions have a positive answer, then
predicate is primitive recursive in the sense that there is a primitive recursive function that, given inputs for the predicate, correctly determines the truth value of the predicate on those inputs.
There is a corresponding primitive recursive function
returns the output of the function with index
Because Kleene's formalism attaches a number of inputs to each function, the predicate
can only be used for functions that take one input.
There are additional predicates for functions with multiple inputs; the relation is true if
encodes a halting computation of the function with index
Because of this, any theory of arithmetic that is able to represent every primitive recursive function is able to represent
Examples of such arithmetical theories include Robinson arithmetic and stronger theories such as Peano arithmetic.
predicates can be used to obtain Kleene's normal form theorem for computable functions (Soare 1987, p. 15; Kleene 1943, p. 52—53).
This states there exists a fixed primitive recursive function
is the smallest natural number for which
is true if both sides are undefined or if both are defined and they are equal.
By the theorem, the definition of every general recursive function f can be rewritten into a normal form such that the μ operator is used only once, viz.
, which is independent of the computable function
In addition to encoding computability, the T predicate can be used to generate complete sets in the arithmetical hierarchy.
In particular, the set which is of the same Turing degree as the halting problem, is a
complete unary relation (Soare 1987, pp.
Thus, once a representation of the Tn predicate is obtained in a theory of arithmetic, a representation of a
This construction can be extended higher in the arithmetical hierarchy, as in Post's theorem (compare Hinman 2005, p. 397).