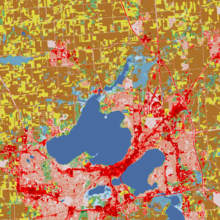
Land cover
Land covers include flora, concrete, built structures, bare ground, and temporary water.
Earth cover is the expression used by ecologist Frederick Edward Clements that has its closest modern equivalent being vegetation.
[2] There are two primary methods for capturing information on land cover: field survey, and analysis of remotely sensed imagery.
One of the major land cover issues (as with all natural resource inventories) is that every survey defines similarly named categories in different ways.
[5] Following table is Land Cover statistics by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) with 14 classes.