Life insurance
Often, specific exclusions written into the contract limit the liability of the insurer; common examples include claims relating to suicide, fraud, war, riot, and civil commotion.
[2] Life-based contracts tend to fall into two major categories: An early form of life insurance dates to Ancient Rome; "burial clubs"[3] covered the cost of members' funeral expenses and assisted survivors financially.
In 1816, an archeological excavation in Minya, Egypt (under an Eyalet of the Ottoman Empire) produced a Nerva–Antonine dynasty-era tablet from the ruins of the Temple of Antinous in Antinoöpolis, Aegyptus that prescribed the rules and membership dues of a burial society collegium established in Lanuvium, Italia in approximately 133 AD during the reign of Hadrian (117–138) of the Roman Empire.
[4] In 1851, future U.S. Supreme Court Associate Justice Joseph P. Bradley (1870–1892), once employed as an actuary for the Mutual Benefit Life Insurance Company, submitted an article to the Journal of the Institute of Actuaries detailing an historical account of a Severan dynasty-era life table compiled by the Roman jurist Ulpian in approximately 220 AD during the reign of Elagabalus (218–222) that was included in the Digesta seu Pandectae (533) codification ordered by Justinian I (527–565) of the Eastern Roman Empire.
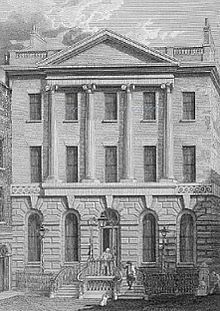
[6][7] The first company to offer life insurance in modern times was the Amicable Society for a Perpetual Assurance Office, founded in London in 1706 by William Talbot and Sir Thomas Allen.
At the end of the year a portion of the "amicable contribution" was divided among the wives and children of deceased members, in proportion to the number of shares the heirs owned.
[12] The Society sought to treat its members equitably and the Directors tried to ensure that policyholders received a fair return on their investments.
The insurable interest requirement usually demonstrates that the purchaser will actually suffer some kind of loss if the CQV dies.
The insurance company calculates the policy prices (premiums) at a level sufficient to fund claims, cover administrative costs, and provide a profit.
As people are more likely to die as they get older, the mortality tables enable insurance companies to calculate the risk and increase premiums with age accordingly.
[17] The mortality tables provide a baseline for the cost of insurance, but the health and family history of the individual applicant is also taken into account (except in the case of Group policies).
[24] These systems allow point of sale distribution and can shorten the time frame for issuance from weeks or even months to hours or minutes, depending on the amount of insurance being purchased.
Consequently, in a group of one thousand 25-year-old males with a $100,000 policy, all of average health, a life insurance company would have to collect approximately $50 a year from each participant to cover the relatively few expected claims.
The amount of the death benefit is typically determined at the time the policy is purchased, and it is based on factors such as the policyholder's age, health, and occupation.
In general, in jurisdictions where both terms are used, "insurance" refers to providing coverage for an event that might happen (fire, theft, flood, etc.
In the United States, both forms of coverage are called "insurance" for reasons of simplicity in companies selling both products.
The endowment policy is a life insurance contract designed to pay a lump sum after a specific term (on its 'maturity') or on death.
"Accidents" run the gamut from abrasions to catastrophes but normally do not include deaths resulting from non-accident-related health problems or suicide.
In an AD&D policy, benefits are available not only for accidental death but also for the loss of limbs or body functions such as sight and hearing.
If a rider is purchased, the policy generally pays double the face amount if the insured dies from an accident.
The policy's death benefit is initially based on the funeral cost at the time of prearrangement, and it then typically grows as interest is credited.
Along with life insurance premiums, section 80C allows an exemption for other financial instruments such as Employee Provident Fund (EPF), Public Provident Fund (PPF), Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS), National Savings Certificate (NSC), and health insurance premiums are some of them.
In 2018, a fiduciary standard rule on retirement products by the United States Department of Labor posed a possible risk.
Single premium contracts and those running for a short term are subject to income tax depending upon the marginal rate in the year a gain is made.
Therefore, a policyholder who is a higher-rate taxpayer (40% in 2005-06), or becomes one through the transaction, must pay tax on the gain at the difference between the higher and the lower rate.
This gain is reduced by applying a calculation called top-slicing based on the number of years the policy has been held.
The withdrawal is deemed by the HMRC (Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs) to be a payment of capital and therefore, the tax liability is deferred until maturity or surrender of the policy.
[35] Multiple fictional and non-fictional works, including books, films, television series and podcasts have featured the scenario as a plot device or actually occurring as a true crime.
After the contestability period ended on the policies, the women are alleged to have had the men killed via hit-and-run vehicular homicide.
[36] On April 17, 2016, a report by Lesley Stahl on 60 Minutes claimed that life insurance companies do not pay significant numbers of beneficiaries.