Light scattering by particles
Light scattering by particles is the process by which small particles (e.g. ice crystals, dust, atmospheric particulates, cosmic dust, and blood cells) scatter light causing optical phenomena such as the blue color of the sky, and halos.
In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized and solved.
The relative size of a scattering particle is defined by its size parameter x, which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension to its wavelength: The FDTD method belongs in the general class of grid-based differential time-domain numerical modeling methods.
The resulting finite-difference equations are solved in either software or hardware in a leapfrog manner: the electric field vector components in a volume of space are solved at a given instant in time; then the magnetic field vector components in the same spatial volume are solved at the next instant in time; and the process is repeated over and over again until the desired transient or steady-state electromagnetic field behavior is fully evolved.
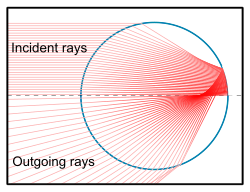
The light can be considered as a collection of rays whose widths are much larger than the wavelength but small compared to the particle itself.
Just as with lenses and other optical components, ray tracing determines the light emanating from a single scatterer, and combining that result statistically for a large number of randomly oriented and positioned scatterers, one can describe atmospheric optical phenomena such as rainbows due to water droplets and halos due to ice crystals.