Linear polarization
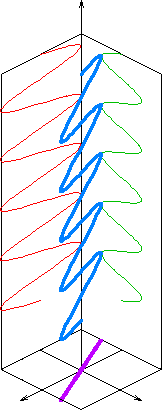
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation.
The term linear polarization (French: polarisation rectiligne) was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.
The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave is defined by the direction of the electric field vector.
is the amplitude of the field and is the Jones vector in the x-y plane.
If unit vectors are defined such that and then the polarization state can be written in the "x-y basis" as This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C.