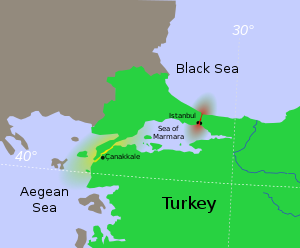
London Straits Convention
In the London Straits Convention concluded on 13 July 1841 between the Great Powers of Europe at the time—Russia, the United Kingdom, France, Austria and Prussia—the "ancient rule" of the Ottoman Empire was re-established by closing the Turkish Straits (the Bosporus and Dardanelles), which link the Black Sea to the Mediterranean, from all warships whatsoever, barring those of the Sultan's allies during wartime.
It evolved as a reaction to the secret article in the Treaty of Hünkâr İskelesi (Unkiar Skelessi), created in 1833, in which the Ottoman Empire guaranteed exclusive use of the straits to Ottoman and Imperial Russian warships in the case of a general war, allowing no "foreign vessels of war to enter therein under any pretext whatsoever".
[citation needed] He also authorised the British Navy to quell the attack on the Ottoman Empire by its former vassal, Muhammad Ali.
From the Russian point of view, the treaty encouraged the aggressive policies of Britain in the region, which would lead to the Crimean War.
[citation needed] Different interpretations, as well as history of British-Russian relations in the 1840s, suggest that the Straits Convention 'appeared to establish a new era of harmony' between both powers, keeping Russian navy out of the Mediterranean and British out of the Black Sea.