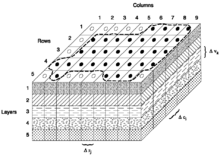
MODFLOW
The source code is free public domain software,[1] written primarily in Fortran, and can compile and run on Microsoft Windows or Unix-like operating systems.
Since its original development in the early 1980s,[2] the USGS has made six major releases, and is now considered to be the de facto standard code for aquifer simulation.
At the time, it was common practice to rewrite a new model to fit the need of a new groundwater scenario.
The source code for this version is listed in USGS Open File Report 83-875 referred to above.
MODPATH, was initially developed in 1989 to post-process the steady-state MODFLOW-88 data to determine three-dimensional pathlines of particles.
The internal design concepts also changed from previous versions, such that packages, processes and modules are distinct.
There are four related or branched codes based on MODFLOW-2000: MODFLOW-2005 [8] differs from MODFLOW-2000 in that the sensitivity analysis, parameter estimation, and uncertainty evaluation capabilities are removed.
In addition, the code was reorganized to support multiple models within one MODFLOW run, as needed for the LGR (Local Grid Refinement) capability.
[18] The names in this table are the labels used to turn MODFLOW capabilities on and off via a key input file.
Many of the capabilities introduced are supported in later versions, though the grid change enabled with MODFLOW-USG and MODFLOW 6 meant that such backward compatibility was rather selective.
Non-commercial MODFLOW versions are free, however, their licensing usually limit the use to non-profit educational or research purposes.
Professional versions of MODFLOW are generally priced at a minimum of around $1000 and typically range upward to US$7000.