Macular degeneration
[1] While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life.
Those with dry-form AMD have drusen, cellular debris in their macula that gradually damages light-sensitive cells and leads to vision loss.
[1] In the wet form, anti–vascular endothelial growth factor injected into the eye or, less commonly, laser coagulation or photodynamic therapy may slow worsening.
[citation needed] In Caucasian (white) skin, there is a specific group of polymorphic genes (with single nucleotide alterations) that encode for enzymes and transcription factors responsible for the early steps (including the first step, formation of L-DOPA from the amino acid tyrosine) of the melanin synthesis pathway.
[18] Recurrence ratios for siblings of an affected individual are three- to six-fold higher than in the general population.
[33] Genetic linkage analysis has identified 5 sets of gene variants at three locations on different chromosomes (1, 6 and 10) as explaining at least 50% of the risk.
[18][48][49][50][51][52] Thus an AMD pathophysiological model of chronic low grade complement activation and inflammation in the macula has been advanced.
The early stigmata of the disease, drusen, are rich in cholesterol, offering face validity to the results of genome-wide association studies.
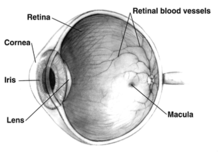
[57] In AMD there is a progressive accumulation of characteristic yellow deposits, called drusen (buildup of extracellular proteins and lipids), in the macula (a part of the retina), between the retinal pigment epithelium and the underlying choroid.
[58] AMD can be divided into 3 stages: early, intermediate, and late, based partially on the extent (size and number) of drusen.
[1] AMD-like pathology begins with small yellow deposits (drusen) in the macula, between the retinal pigment epithelium and the underlying choroid.
The risk of developing symptoms is higher when the drusen are large and numerous, and associated with the disturbance in the pigmented cell layer under the macula.
[citation needed] Early AMD is diagnosed based on the presence of medium-sized drusen, which is about the width of an average human hair.
[citation needed] In late AMD, enough retinal damage occurs that, in addition to drusen, people will also begin to experience symptomatic central vision loss.
Dry AMD patients tend to have minimal symptoms in the earlier stages; visual function loss occurs more often if the condition advances to geographic atrophy.
Some studies questioned whether it was due to a deficient retinal pigment epithelium, leading to increased oxidative stress.
They found that decreased blood flow in the choriocapillaris precedes atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium and the overlying photoreceptors.
[64] Since the choriocapillaris is a vascular layer, this may be used as an argument for why geographic atrophy could be a disease due to decreased blood flow.
Bleeding, leaking, and scarring from these blood vessels eventually cause irreversible damage to the photoreceptors and rapid vision loss if left untreated.
[69] The CNV present in wet AMD is managed with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors.
[2] AREDS supplementation may help slow the progression to more severe forms of AMD[5] and there is some evidence of improved visual acuity at 5 years.
The clinical development of this mechanism, which has the potential to clear Bruch's membrane and reduce the formation of drusen, is in preparation.
[citation needed] Ranibizumab, aflibercept, brolucizumab, and faricimab are approved VEGF inhibitors for the treatment of CNV in wet AMD.
[79] A 2014 Cochrane review found that the systemic safety of bevacizumab and ranibizumab are similar when used to treat neovascular AMD, except for gastrointestinal disorders.
In the case of pro re nata, the patient comes at fixed intervals, but treatment is only administered if an activity is detected (i.e., the presence of fluid).
[86][87][88] The American Academy of Ophthalmology practice guidelines do not recommend laser coagulation therapy for macular degeneration, but state that it may be useful in people with new blood vessels in the choroid outside of the fovea who do not respond to drug treatment.
[95] Nucleoside reverse transcription inhibitors like they are used in anti-HIV therapy were associated with a reduced risk of developing atrophic macular degeneration.
[104] Genetic testing can help identify whether a patient with AMD is at a greater risk of developing the condition and can inform disease progression.
[18] Genetic testing can also allow researchers to identify whether patients are more or less likely to respond to treatments, such anti-VEGF medication or complement inhibitors.
It secretes a large variety of factors including at least 22 proteins important in maintaining the structure, function and micro-environments on the two sides of the RPE.