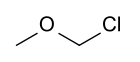
Chloromethyl methyl ether
A similar method, using a high-boiling acyl chloride, can be used to prepare pure, dimethoxymethane being the only contaminant.
[6] In contrast, the classical procedure reported in Organic Syntheses employing formaldehyde, methanol, and hydrogen chloride yields material significantly contaminated with the dangerous bis(chloromethyl) ether and requires fractional distillation.
[8] Chronic exposure can increase the incidence of respiratory cancers, including small cell carcinoma.
[9] It is one of 13 chemicals regulated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration despite not having an established permissible exposure limit.
11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.