Methylmalonic acidemias
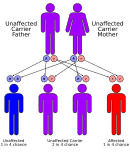
[2] Methylmalonic acidemias have varying diagnoses, treatment requirements and prognoses, which are determined by the specific genetic mutation causing the inherited form of the disorder.
[citation needed] The exception is methylmalonic acidemia and homocystinuria, cblX type due to variants in HCFC1 gene, which is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner.
Those afflicted with this disorder are either lacking functional copies or adequate levels of one or more of the following enzymes:[6][11][9] These are briefly introduced below: It is estimated that as many as 60% of isolated methylmalonic acidemia cases are the result of a mutated MMUT gene which encodes the protein methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
The action of this enzyme can also be crippled by mutations in the MMAA, MMAB, and MMADHC genes, each of which encodes a protein required for normal functioning of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
[10][45] For this purpose, a dried blood spot test for the parameter propionylcarnitine (C3) is carried out at the age of 24–48 hours in order to detect isolated methylmalonic acidemias.
[13][46] Due to normal propionylcarnitine levels and asymptomatic symptoms at the time of testing, the probably most common form of methylmalonic acidemias, CMAMMA, slips through the newborn screening.
Due to their high sensitivity, easier accessibility and non-invasiveness, molecular genetic tests replace enzyme assays in most cases.
[52] The presence of methylmalonic acidemia can also be suspected through the use of a CT or MRI scan, however these tests are by no means specific and require clinical and metabolic/correlation.
[10] cblDv2 Treatment for all forms of this condition primarily relies on a low-protein diet, and depending on what variant of the disorder the individual suffers from, various dietary supplements.
[53] If the individual proves responsive to both cobalamin and carnitine supplements, then it may be possible for them to ingest substances that include small amounts of the problematic amino acids isoleucine, threonine, methionine, and valine without causing an attack.
[54][40] Preclinical proof-of-concept studies in animal models have shown that mRNA therapy is also suitable for rare metabolic diseases, including isolated methylmalonic acidemia.
[60][59] Another small molecule therapeutic in development is BBP-671 from BridgeBio Pharma for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN), propionic and methylmalonic acidemia, which is currently in phase 1.
If the triggering proteins and fats are not removed from the diet, this buildup can lead to irreparable kidney or liver damage and eventually death.
[10] Despite these challenges, since it was first identified in 1967, treatment and understanding of the condition has improved to the point where it is not unheard of for even those with unresponsive forms of methylmalonic acidemia to be able to reach adulthood and even carry and deliver children safely.
[64] Furthermore, micro-array analysis of these treated neurons have also suggested that on an epigenetic-level methylmalonic acid alters the transcription rate of 564 genes, notably including those involved in the apoptosis, p53, and MAPK signaling pathways.
[64] As the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA takes place inside the mitochondria, mitochondrial dysfunction as a result of diminished electron transport chain function has long been suspected as a feature in methylmalonic acidemias.
Similar changes were identified in the mitochondria of a liver sample removed during transplant from a 5-year-old boy suffering from methylmalonic acidemia mut type.
[66] Despite consistently showing elevated methylmalonic acid in the blood and urine, these individuals appeared for the large part developmentally normal.