Migraine
Migraine (UK: /ˈmiːɡreɪn/, US: /ˈmaɪ-/)[1][2] is a genetically-influenced complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea and light and sound sensitivity.
[6][7] Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influence the excitation and inhibition of nerve cells in the brain.
[17][18] Non-pharmacological preventive therapies include nutritional supplementation, dietary interventions, sleep improvement, and aerobic exercise.
[19] In 2018, the first medication (Erenumab) of a new class of drugs specifically designed for migraine prevention called calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonists (CGRPs) was approved by the FDA.
[22] In the Global Burden of Disease Study, conducted in 2010, migraine ranked as the third-most prevalent disorder in the world.
[32] Prodromal or premonitory symptoms occur in about 60% of those with migraine,[33][34] with an onset that can range from two hours to two days before the start of pain or the aura.
[42] Visual disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma (an area of partial alteration in the field of vision which flickers and may interfere with a person's ability to read or drive).
[41] Other symptoms of the aura phase can include speech or language disturbances, world spinning, and less commonly motor problems.
[54][55] However, silent migraine can still produce debilitating symptoms, with visual disturbance, vision loss in half of both eyes, alterations in color perception, and other sensory problems, like sensitivity to light, sound, and odors.
The person may feel tired or "hung over" and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness.
[72] Another genetic disorder associated with migraine is CADASIL syndrome or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy.
[85][86] There are many reports[87][88][89][90][91] that tyramine – which is naturally present in chocolate, alcoholic beverages, most cheeses, processed meats, and other foods – can trigger migraine symptoms in some individuals.
[93] A 2009 review on potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded that while there were insufficient studies to confirm environmental factors as causing migraine, "migraineurs worldwide consistently report similar environmental triggers ... such as barometric pressure change, bright sunlight, flickering lights, air quality and odors".
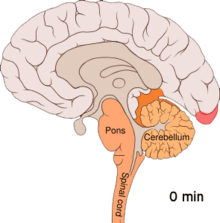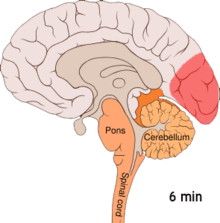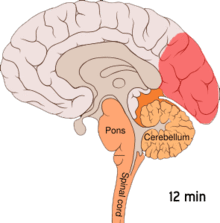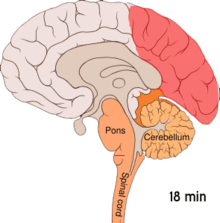
[101][102][11][103] One theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex and abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.
[114] Calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as levels of it become elevated during an attack.
[116] In those with four out of five of the following: pulsating headache, duration of 4–72 hours, pain on one side of the head, nausea, or symptoms that interfere with the person's life, the probability that this is a migraine attack is 92%.
[13] Temporal arteritis typically occurs in people over 50 years old and presents with tenderness over the temple, cluster headache presents with one-sided nose stuffiness, tears and severe pain around the orbits, acute glaucoma is associated with vision problems, meningitis with fevers, and subarachnoid hemorrhage with a very fast onset.
[130] Similarly for children and adolescents, CBT and biofeedback strategies have shown effective in a decrease of frequency and intensity of migraines.
These techniques often include relaxation methods and promotion of long-term management without medication side effects which is emphasized for younger individuals.
[131] Acute treatments, including NSAIDs and triptans, are most effective when administered early in an attack, while preventive medications are recommended for those experiencing frequent or severe migraines.
Proven preventive options include beta blockers, topiramate, and CGRP inhibitors like erenumab and galcanezumab, which have demonstrated significant efficacy in clinical studies.
[132] The European Consensus Statement provides a framework for diagnosis and management, emphasizing the importance of accurate assessment, patient education, and consistent adherence to prescribed treatments.
Innovative therapies of oral medications used to treat migraine symptoms, such as gepants and ditans, are emerging as alternatives for patients who cannot use traditional options.
"[137] "One of the most important problems in clinical migraine is the progression from an intermittent, self-limited inconvenience to a life-changing disorder of chronic pain, sensory amplification, and autonomic and affective disruption.
[144] People with migraine, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance.
[154] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting.
[155] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen, which she described as "reflections of the living light", are consistent with the visual aura experienced during migraine attacks.
[160] The association between trepanation and headaches in ancient history may simply be a myth or unfounded speculation that originated several centuries later.
However, Osler wanted to make Broca's theory more palatable to his modern audiences, and explained that trepanation procedures were used for mild conditions such as "infantile convulsions headache and various cerebral diseases believed to be caused by confined demons.
[170][171] The Society for Women's Health Research has also mentioned hormonal influences, mainly estrogen, as having a considerable role in provoking migraine pain.