Mobile phone feature
[clarification needed] Handsets with more advanced computing ability through the use of native code try to differentiate their own products by implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers.
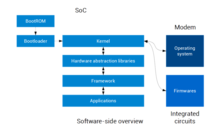
In early stages, every mobile phone company had its own user interface, which can be considered as "closed" operating system, since there was a minimal configurability.
Other capabilities like Pulling and Pushing Emails or working with calendar were also made more accessible but it usually required physical (and not wireless) Syncing.
In July 2008, Apple introduced its App store, which made downloading mobile applications more accessible.
In October 2008, the HTC Dream was the first commercially released device to use the Linux-based Android OS, which was purchased and further developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance to create an open competitor to other major smartphone platforms of the time (Mainly Symbian operating system, BlackBerry OS, and iOS)-The operating system offered a customizable graphical user interface and a notification system showing a list of recent messages pushed from apps.
[11][12][13] A popular early mobile phone battery was the nickel metal-hydride (NiMH) type, due to its relatively small size and low weight.
[14] GSM mobile phones require a small microchip called a Subscriber Identity Module or SIM card, to function.
The SIM card is approximately the size of a small postage stamp and is usually placed underneath the battery in the rear of the unit.
A SIM card contains its unique serial number, internationally unique number of the mobile user (IMSI), security authentication and ciphering information, temporary information related to the local network, a list of the services the user has access to and two passwords (PIN for usual use and PUK for unlocking).
[15][16] From 2010 onwards they became popular in India and Indonesia and other emerging markets,[17] attributed to the desire to obtain the lowest on-net calling rate.
In Q3 2011, Nokia shipped 18 million of its low cost dual SIM phone range in an attempt to make up lost ground in the higher end smartphone market.
The screen size varies greatly by model and is usually specified either as width and height in pixels or the diagonal measured in inches.
[19] Artificial intelligence is the hot center of the technology industry, especially with the introduction of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Gemini.
Read more here: Mobile phones have central processing units (CPUs), similar to those in computers, but optimised to operate in low power environments.
Other features that may be found on mobile phones include GPS navigation, music (MP3) and video (MP4) playback, RDS radio receiver, built-in projector, vibration and other "silent" ring options, alarms, memo recording, personal digital assistant functions, ability to watch streaming video, video download, video calling, built-in cameras (1.0+ Mpx) and camcorders (video recording), with autofocus[dubious – discuss] and flash, ringtones, games, PTT, memory card reader (SD), USB (2.0), dual line support, infrared, Bluetooth (2.0) and WiFi connectivity, NFC, instant messaging, Internet e-mail and browsing and serving as a wireless modem.
The first smartphone was the Nokia 9000 Communicator [dubious – discuss] in 1996 which added PDA functionality to the basic mobile phone at the time.
[21] Some phones have an electromechanical transducer on the back which changes the electrical voice signal into mechanical vibrations.
[23] Most mobile phone networks are digital and use the GSM, CDMA or iDEN standard which operate at various radio frequencies.
The special challenge involved in producing a multi-mode mobile is in finding ways to share the components between the different standards.
The radio interfaces are very different from each other, but mobile to core network messaging has strong similarities, meaning that software sharing is quite easy.
This mode allows for safe inter-frequency handovers with channel measurements which can only be approximated using "pilot signals" in other CDMA based systems.
such as SMS messages, browsing mobile web sites, and even streaming audio and video files.
The main limiting factors are the size of the screen, lack of a keyboard, processing power and connection speed.
Most cellphones, which supports data communications, can be used as wireless modems (via cable or bluetooth), to connect computer to internet.
Later was introduced GPRS (general packet radio service), which operates on completely different principle.
A virus may allow unauthorized users to access a phone to find passwords or corporate data stored on the device.
[citation needed] Mobile phones used to have proprietary operating system unique only to the manufacturer which had the beneficial effect of making it harder to design a mass attack.
In early November 2004, several web sites began offering a specific piece of software promising ringtones and screensavers for certain phones.
The Commwarrior-A virus was identified in March 2005, and it attempts to replicate itself through MMS to others on the phone's contact list.
Like Cabir, Commwarrior-A also tries to communicate via Bluetooth wireless connections with other devices, which can eventually lead to draining the battery.