Mollicutes
Acholeplasmatales Anaeroplasmatales Entomoplasmatales Haloplasmatales Mycoplasmatales Mollicutes is a class of bacteria[2] distinguished by the absence of a cell wall.
Many cause diseases in humans, attaching to cells in the respiratory or urogenital tracts, particularly species of Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma.
By adopting a parasitic mode of life with use of nutrients from their hosts, many Mollicutes were able to reduce their genetic material considerably.
In 1954, this mode of proliferation has been shown by continual observations of live cells using phase-contrast microscopy.
At first, all members of the class Mollicutes were generally named "mycoplasma" or pleuropneumonia-like organism (PPLO).
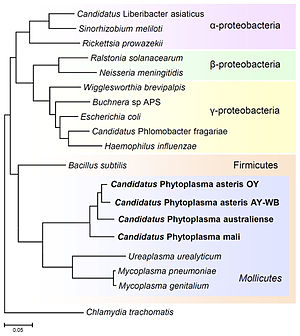
Murray proposed to divide the "kingdom" (now domain[8]) Bacteria into three divisions (= phyla) on the basis of the cell wall types: For classification and nomenclature of Mollicutes, there are special rules, which are maintained by the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (ICSP) Subcommittee on the Taxonomy of Mollicutes (formerly the International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology (ICSB) Subcommittee on taxonomy of Mycoplasmatales).
They concluded, that the Mollicutes are not a phylogenetically coherent group and therefore do not form a distinct higher level taxon.
[12] Phylogenetic trees based on phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk) amino acid sequences' indicated a monophyletic origin for the Mollicutes within the Bacillota.
[16][17][18] The change is motivated by "their unique phenotypic properties, in particular the lack of rigid cell walls, and the general low support by alternative markers".
[12] In the Taxonomic Outline of Bacteria and Archaea (TOBA Release 7.7), March 2007, the Mollicutes are a class in the phylum Bacillota.
[19] The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[20] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[21] other Lottiidibacillus Culicoidibacter Haloplasma ♦ Turicibacter other Fusobacteriales Asteroleplasma ♦ Coprobacillaceae Erysipelotrichaceae ♦ Acholeplasmataceae (incl.
Acholeplasmataceae "Aphodocolaceae" [RF39] "Caccosomataceae" "Enterosomataceae" "Enteromonadaceae" Coprobacillaceae Erysipelotrichaceae Spiroplasma species-group 3 {VBWQ01} Mycoplasmataceae (incl.