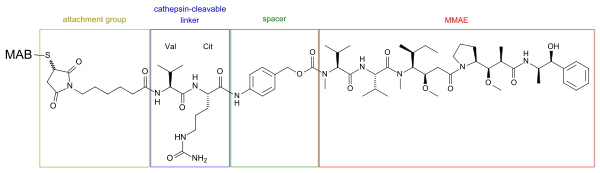
Monomethyl auristatin E
Because of its toxicity, it cannot be used as a drug itself; instead, it is linked to a monoclonal antibody (MAB) which directs it to the cancer cells.
[1] It is a potent antimitotic drug derived from peptides occurring in marine shell-less mollusc Dolabella auricularia called dolastatins which show potent activity in preclinical studies, both in vitro and in vivo, against a range of lymphomas, leukemia and solid tumors.
[2] MMAE is actually desmethyl-auristatin E; that is, the N-terminal amino group has only one methyl substituent instead of two as in auristatin E itself.
[2] Monomethyl auristatin E is an antimitotic agent which inhibits cell division by blocking the polymerisation of tubulin.
The linker to the monoclonal antibody is stable in extracellular fluid, but is cleaved by cathepsin once the conjugate has entered a tumor cell, thus activating the antimitotic mechanism.