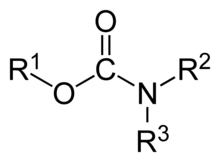
Carbamate
[7] Within nature carbon dioxide can bind with neutral amine groups to form a carbamate, this post-translational modification is known as carbamylation.
[8] The N-terminal amino groups of valine residues in the α- and β-chains of deoxyhemoglobin exist as carbamates.
[11] Although not usually isolated as such, the salt ammonium carbamate is produced on a large scale as an intermediate in the production of the commodity chemical urea from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
[citation needed] Polyurethane polymers have a wide range of properties and are commercially available as foams, elastomers, and solids.
Included in this group are aldicarb (Temik), carbofuran (Furadan), carbaryl (Sevin), ethienocarb, fenobucarb, oxamyl, and methomyl.
These insecticides kill insects by reversibly inactivating the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE inhibition)[13] (IRAC mode of action 1a).
[14] The organophosphate pesticides also inhibit this enzyme, although irreversibly, and cause a more severe form of cholinergic poisoning[15] (the similar IRAC MoA 1b).
Other carbamate based acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are known with even higher toxicity to humans, and some such as T-1123 and EA-3990 were investigated for potential military use as nerve agents.
However, since all compounds of this type have a quaternary ammonium group with a permanent positive charge, they have poor blood–brain barrier penetration, and also are only stable as crystalline salts or aqueous solutions, and so were not considered to have suitable properties for weaponisation.
Urethane (ethyl carbamate) was once produced commercially in the United States as a chemotherapy agent and for other medicinal purposes.
[28] In addition, some carbamates are used in human pharmacotherapy, for example, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors neostigmine and rivastigmine, whose chemical structure is based on the natural alkaloid physostigmine.
Other examples are meprobamate and its derivatives like carisoprodol, felbamate, mebutamate, phenprobamate, and tybamate, a class of anxiolytic and muscle relaxant drugs widely used in the 1960s before the rise of benzodiazepines, and still used nowadays in some cases.
The new ether, brought into contact with liquid and concentrated ammonia, exerts on this substance a reaction so strong that the mixture boils, and sometimes even produces a sort of explosion.
However, later Dumas states "While waiting for opinion to settle on the nature of this body, I propose to designate by the names of urethane and oxamethane the two materials which I have just studied, and which I regard as types of a new family, among nitrogenous substances.
These names which, in my eyes, do not prejudge anything in the question of alcohol and ethers, will at least have the advantage of satisfying chemists who still refuse to accept our theory.
[41] Medlock states "It is well known that the action of ammonia on chloro-carbonate (phosgene) of ethyl gives rise to the formation of the substance which Dumas, the discoverer, called urethane, and which we are now in the habit of considering as the ether of carbamic acid.