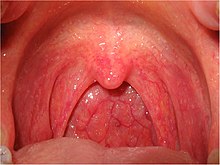
Pharynx
: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively).
The opening and closing of the auditory tubes serves to equalize the barometric pressure in the middle ear with that of the ambient atmosphere.
Two folds arise from the cartilaginous opening: The oropharynx lies behind the oral cavity, extending from the uvula to the level of the hyoid bone.
The HACEK organisms (Haemophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella) are part of the normal oropharyngeal flora, which grow slowly, prefer a carbon dioxide-enriched atmosphere, and share an enhanced capacity to produce endocardial infections, especially in young children.
Corresponding roughly to the area located between the 4th and 6th cervical vertebrae, the superior boundary of the laryngopharynx is at the level of the hyoid bone.
The laryngopharynx includes three major sites: the pyriform sinus, postcricoid area, and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Like the oropharynx above it, the laryngopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium.
Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an anatomical term collectively describing the annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx.
Waldeyer's ring circumscribes the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate (and to the back of the oral cavity).
It is believed that Waldeyer's ring prevents the invasion of microorganisms from going into the air and food passages and this helps in the defense mechanism of the respiratory and alimentary systems.
These outpocketings are pharyngeal arches, and they give rise to a number of different structures in the skeletal, muscular, and circulatory systems.
In the horse, the auditory tube opens into the guttural pouch and the tonsils are diffuse and raised slightly.
However, the vertebrate pharynx is unique in that it gives rise to endoskeletal support through the contribution of neural crest cells.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1141 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918) General