Geography of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The country's natural resources include coal, iron ore, bauxite, manganese, nickel, clay, gypsum, salt, sand, timber and hydropower.
Northern Bosnia contains very fertile agricultural land along the river Sava and the corresponding area is heavily farmed.
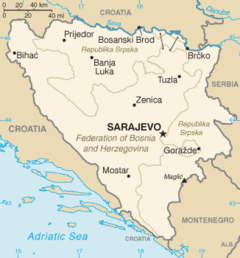
The northwest part of Bosnia is called Bosanska Krajina and holds the cities of Banja Luka, Prijedor, Sanski Most, Jajce, Cazin, Velika Kladuša and Bihać.
Kozara National Park and Mrakovica World War II monument is located in this region.
Most important of these is the so-called area of “central Bosnian mountains” located between the rivers Vrbas, Lašva, Neretva, Rama and their tributaries.
The second one is the area of western Bosnia, bordered by the Vrbas and Una rivers, with its main orebearing formations found in the river-valleys of Sana and Japra, and their tributaries.
The third area is eastern Bosnia, around the river Drina between the towns of Foča and Zvornik, the principal mining activity centered around Srebrenica.
Ores of various metals, including iron, are found in these areas and exploitation has been going on for more than 5000 years – from the period of prehistoric human settlers, through Illyrian, Roman, Slavic, Turkish and Austrian rulers, into the present.