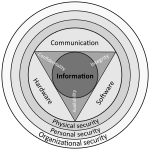
Network security
[2][3] Though effective to prevent unauthorized access, this component may fail to check potentially harmful content such as computer worms or Trojans being transmitted over the network.
Anti-virus software or an intrusion prevention system (IPS)[4] help detect and inhibit the action of such malware.
An anomaly-based intrusion detection system may also monitor the network like wireshark traffic and may be logged for audit purposes and for later high-level analysis.
Newer systems combining unsupervised machine learning with full network traffic analysis can detect active network attackers from malicious insiders or targeted external attackers that have compromised a user machine or account.
However, more recently, the discussion has expanded to consider information security in the broader context of the digital economy and society.
This indicates that it's not just about individual users and tools; it's also about the larger culture of information security in our digital world.
Andersson and Reimers (2014) found that employees often do not see themselves as part of their organization's information security effort and often take actions that impede organizational changes.