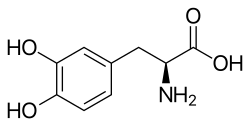
Neurotransmitter prodrug
[1][2] They can be useful when the neurotransmitter itself is not suitable for use as a pharmaceutical drug owing to unfavorable pharmacokinetic or physicochemical properties, for instance high susceptibility to metabolism, short elimination half-life, or lack of blood–brain barrier permeability.
[6][7][8] Other dopamine prodrugs, including etilevodopa, foslevodopa, melevodopa, XP-21279, DopAmide, DA-Phen, O,O'-diacetyldopamine, O,O'-dipivaloyldopamine, docarpamine, gludopa, and gludopamine, have also been developed.
[16][17][18] 5-HTP is additionally a prodrug of N-methylated tryptamine psychedelic trace amines, such as N-methylserotonin (NMS; norbufotenin) and bufotenin (5-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine; 5-HO-DMT).
[20][24][25][26][27] Dependent on these transformations, both tryptophan and 5-HTP produce the head-twitch response (HTR), a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, at sufficiently high doses in animals.
[20][28][29][21][30][19] O-Acetylbufotenine and O-pivalylbufotenine are thought to be centrally active prodrugs of the peripherally selective bufotenin.