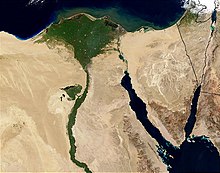
Nile Delta
[1] It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers 240 km (150 mi) of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region.
Since the delta no longer receives an annual supply of nutrients and sediments from upstream due to the construction of the Aswan Dam, the soils of the floodplains have become poorer, and large amounts of fertilizers are now used.
In July 2019 a small Greek temple, ancient granite columns, treasure-carrying ships, and bronze coins from the reign of Ptolemy II, dating back to the third and fourth centuries BC, were found at the sunken city of Heracleion, colloquially known as Egypt's Atlantis.
[7][8][9][10] In January 2019 archaeologists led by Mostafa Waziri working in the Kom Al-Khelgan area of the Nile Delta discovered tombs from the Second Intermediate Period and burials from the Naqada II era.
The burial site contained the remains of animals, amulets and scarabs carved from faience, round and oval pots with handles, flint knives, broken and burned pottery.
[20] Several hundred thousand water birds spend their winter in the delta, including the world's largest concentrations of little gulls and whiskered terns.
Other birds making their homes in the delta include grey herons, Kentish plovers, shovelers, cormorants, egrets and ibises.
[21] Egypt's Mediterranean coastline experiences significant loss of land to the sea, in some places amounting to 90 m (100 yd) a year.
If the polar ice caps were to melt, much of the northern delta, including the ancient port city of Alexandria, could disappear under the Mediterranean.
A 30 cm (12 in) rise in sea level could affect about 6.6% of the total land cover area in the Nile Delta region.
[24] Some areas of the Nile Delta's agricultural land have been rendered saline as a result of sea level rise; farming has been abandoned in some places, while in others sand has been brought in from elsewhere to reduce the effect.