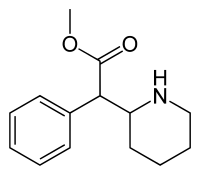
Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor
A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a type of drug that inhibits the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine and thereby increases extracellular levels of these neurotransmitters and noradrenergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission.
[1] NDRIs are used clinically in the treatment of conditions including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and depression.
Examples of well-known NDRIs include methylphenidate and bupropion.
A closely related type of drug is a norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (NDRA).
[3] Norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agents (NDRAs) like amphetamine and methamphetamine not only induce monoamine release but also act as monoamine reuptake inhibitors to a lesser extent and hence are additionally NDRIs.