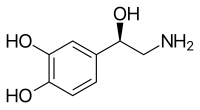
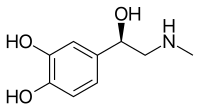
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Additionally, many addictive substances such as cocaine and methylphenidate possess NRI activity, though NRIs without combined dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) properties are not significantly rewarding and hence are considered to have negligible potential for addiction.
[1][2] However, norepinephrine has been implicated as acting synergistically with dopamine when actions on the two neurotransmitters are combined (e.g., in the case of NDRIs) to produce rewarding effects in psychostimulant addictive substances.
[3] A meta analysis published in BMJ in 2011 concluded that the selective NRI reboxetine is indistinguishable from placebo in the treatment of depression.
[4] A second review by the European Medicines Agency concluded that reboxetine was significantly more effective than placebo, and that its risk/benefit ratio was positive.
For a list of NRIs that act at multiple MATs, see the other monoamine reuptake inhibitor pages such as NDRI, SNRI, and SNDRI.