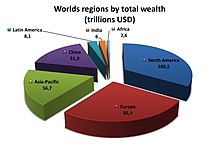
North America
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period.
Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups.
[19] Waldseemüller used the Latinized version of Vespucci's name, Americus Vespucius, in its feminine form of "America", following the examples of "Europa", "Asia", and "Africa".
Americus originated from Medieval Latin Emericus (see Saint Emeric of Hungary), coming from the Old High German name Emmerich.
In a geologic sense, Bermuda is not part of the Americas, but an oceanic island that was formed on the fissure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 100 million years ago (mya).
Mexico, with its long plateaus and cordilleras, falls largely in the western region, although the eastern coastal plain does extend south along the Gulf.
Tropical climates appear in the island regions and in the subcontinent's bottleneck, found in countries and states bathed by the Caribbean Sea or to the south of the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean.
Notable North American fauna include the bison, black bear, jaguar, cougar, prairie dog, turkey, pronghorn, raccoon, coyote, and monarch butterfly.
Notable plants that were domesticated in North America include tobacco, maize, squash, tomato, sunflower, blueberry, avocado, cotton, chile pepper, and vanilla.
From the Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic eras, North America was joined with the other modern-day continents as part of the supercontinent Pangaea, with Eurasia to its east.
Fertile soils from weathered volcanic lavas have made it possible to sustain dense populations in agriculturally productive highland areas.
Anthropologists speculate that the Inuit of the high Arctic arrived in North America much later than other native groups, evidenced by the disappearance of Dorset culture artifacts from the archaeological record and their replacement by the Thule people.
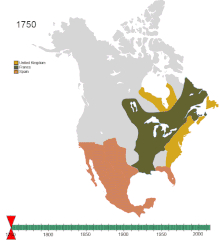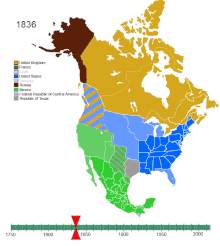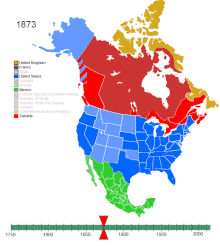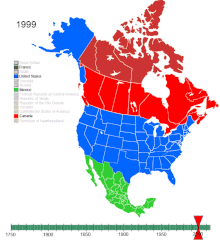
[102] During the so-called Age of Discovery, Europeans explored overseas and staked claims to various parts of North America, much of which was already settled by indigenous peoples.
On North America's southeastern coast, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León, who had accompanied Columbus's second voyage, visited and named in 1513 La Florida.
[105] As the colonial period unfolded, Spain, England, and France appropriated and claimed extensive territories in North America eastern and southern coastlines.
Spain established permanent settlements on the Caribbean islands of Hispaniola and Cuba in the 1490s, building cities, putting the resident indigenous populations to work, raising crops for Spanish settlers and panning gold to enrich the Spaniards.
France took the western half of Hispaniola and developed Saint-Domingue as a cane sugar producing colony worked by black slave labor.
Britain did not begin settling on the North American mainland until a hundred years after the first Spanish settlements, since it sought first to control nearby Ireland.
With the British victory in the Seven Years' War, France in 1763 ceded to Britain its claims of North American territories east of the Mississippi River.
These early French settlers partnered with midwest indigenous tribes, and their mixed ancestry descendants later followed a westward expansion all the way to the Pacific Ocean on the present-day U.S. West Coast.
With the signing and issuance of the Declaration of Independence, the thirteen colonies formalized and escalated the American Revolutionary War, which had begun the year before at the Battles of Lexington and Concord on 19 April 1775.
By the late 18th century, Russia was established on the Pacific Northwest northern coastline, where it was engaged in maritime fur trade and was supported by various indigenous settlements in the region.
After decades of work, the Panama Canal was completed, which connected the Atlantic and Pacific oceans in 1913 and greatly facilitated global shipping navigation.
For example, small Caribbean island-nations, such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, have a higher GDP (PPP) per capita than Mexico due to their smaller populations.
[107] Additionally, despite Greenland's vast resources in oil and minerals, much of them remain untapped, and the island is economically dependent on fishing, tourism, and subsidies from Denmark.
The term Anglo-America is used to refer to the anglophone countries of the Americas: namely Canada (where English and French are co-official) and the U.S., but also sometimes Belize and parts of the tropics, especially the Commonwealth Caribbean.
Cities in the Sun Belt regions of the U.S., such as those in Southern California and Houston, Phoenix, Miami, Atlanta, and Las Vegas, are experiencing rapid growth.
†2011 Census figures North America's GDP per capita was evaluated in October 2016 by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to be $41,830, making it the richest continent in the world,[153] followed by Oceania.
However, they share with the United States the establishment of post-independence governments that are federated representative republics with written constitutions dating from their founding as nations.
Latino culture is strong in the southwestern United States, as well as in the New York metropolitan area and Florida, which draw Latin Americans from many countries in the Western hemisphere.