Dentistry
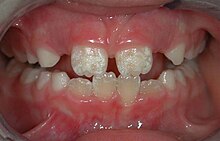
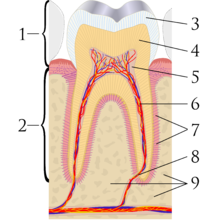
It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa.
[4] Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which reason the two terms are used interchangeably in certain regions.
Other practices relevant to evidence-based dentistry include radiology of the mouth to inspect teeth deformity or oral malaises, haematology (study of blood) to avoid bleeding complications during dental surgery, cardiology (due to various severe complications arising from dental surgery with patients with heart disease), etc.
[6] The term for the associated scientific study of teeth is odontology (from Ancient Greek: ὀδούς, romanized: odoús, lit.
Common treatments involve the restoration of teeth, extraction or surgical removal of teeth, scaling and root planing, endodontic root canal treatment, and cosmetic dentistry[9] By nature of their general training, dentists, without specialization can carry out the majority of dental treatments such as restorative (fillings, crowns, bridges), prosthetic (dentures), endodontic (root canal) therapy, periodontal (gum) therapy, and extraction of teeth, as well as performing examinations, radiographs (x-rays), and diagnosis.
Depending on their licensing boards, general dentists may be required to complete additional training to perform sedation, dental implants, etc.
Dentists also encourage the prevention of oral diseases through proper hygiene and regular, twice or more yearly, checkups for professional cleaning and evaluation.
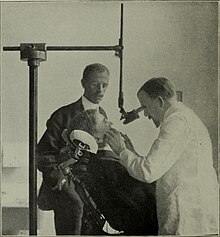
John M. Harris started the world's first dental school in Bainbridge, Ohio, and helped to establish dentistry as a health profession.
[25] The British Dental Association, formed in 1880 with Sir John Tomes as president, played a major role in prosecuting dentists practising illegally.
[37] The Neolithic site of Mehrgarh (now in Pakistan's south western province of Balochistan) indicates that this form of dentistry involved curing tooth related disorders with bow drills operated, perhaps, by skilled bead-crafters.
[39] Dentistry was practised in prehistoric Malta, as evidenced by a skull which had a dental abscess lanced from the root of a tooth dating back to around 2500 BC.
[40] The practice of dentistry dates back thousands of years, with evidence of dental procedures such as tooth extraction and fillings found in ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and the Greeks.
One notable historical figure is Pierre Fauchard, often referred to as the 'father of modern dentistry,' who wrote the first comprehensive book on the subject in 1728.
[48] Use of dental appliances, bridges and dentures was applied by the Etruscans in northern Italy, from as early as 700 BC, of human or other animal teeth fastened together with gold bands.
Roman medical writer Cornelius Celsus wrote extensively of oral diseases as well as dental treatments such as narcotic-containing emollients and astringents.
[54] The earliest dental amalgams were first documented in a Tang dynasty medical text written by the Chinese physician Su Kung in 659, and appeared in Germany in 1528.
[55][56] During the Islamic Golden Age Dentistry was discussed in several famous books of medicine such as The Canon in medicine written by Avicenna and Al-Tasreef by Al-Zahrawi who is considered the greatest surgeon of the Middle Ages,[57] Avicenna said that jaw fracture should be reduced according to the occlusal guidance of the teeth; this principle is still valid in modern times.
[61] The first book focused solely on dentistry was the "Artzney Buchlein" in 1530,[48] and the first dental textbook written in English was called "Operator for the Teeth" by Charles Allen in 1685.
[23] In the United Kingdom, there was no formal qualification for the providers of dental treatment until 1859 and it was only in 1921 that the practice of dentistry was limited to those who were professionally qualified.
1690) made an early dental observation with characteristic humour: The Egyptian Mummies that I have seen, have had their Mouths open, and somewhat gaping, which affordeth a good opportunity to view and observe their Teeth, wherein 'tis not easie to find any wanting or decayed: and therefore in Egypt, where one Man practised but one Operation, or the Diseases but of single Parts, it must needs be a barren Profession to confine unto that of drawing of Teeth, and little better than to have been Tooth-drawer unto King Pyrrhus, who had but two in his Head.The French surgeon Pierre Fauchard became known as the "father of modern dentistry".
The French text included "basic oral anatomy and function, dental construction, and various operative and restorative techniques, and effectively separated dentistry from the wider category of surgery".
Although the donated teeth never properly bonded with the recipients' gums, one of Hunter's patients stated that he had three which lasted for six years, a remarkable achievement for the period.
In the same year, Francis Brodie Imlach was the first ever dentist to be elected President of the Royal College of Surgeons (Edinburgh), raising dentistry onto a par with clinical surgery for the first time.
[67] NIHL can occur when an individual is exposed to sound levels above 90 dBA according to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
[69] While a majority of the tools do not exceed 75 dBA,[70] prolonged exposure over many years can lead to hearing loss or complaints of tinnitus.
Dentistry is unique in that it requires dental students to have competence-based clinical skills that can only be acquired through supervised specialized laboratory training and direct patient care.