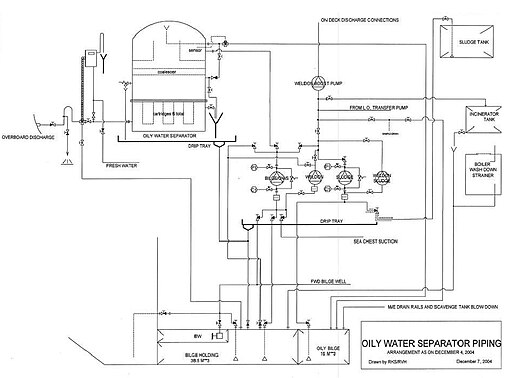
Oily water separator (marine)
Oil leaks from running machinery such as diesel generators, air compressors, and the main propulsion engine.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) publishes regulations through the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC).
This document is known as MEPC 107(49)[3] and it details revised guidelines and specifications for pollution prevention equipment for machinery space bilges of ships.
Here fuels, lubricants, hydraulic fluid, antifreeze, solvents, and cleaning chemicals drain into the engine room bilges in small quantities.
The OWS is intended to remove a large proportion of these contaminants before discharge to the environment (overboard to the sea).
Initially these combinations were very simple, basically no more than a mixture of clean water and diesel fuel, but they have become more sophisticated under MARPOL MEPC 107(49).
[3][4] The vast majority of these many equipment models, manufacturers, and types start with some sort of gravity separation of bilge water.
If the oil content is higher than 15 ppm, the OCM will activate an alarm and move a three-way valve that, within a short period of time, will recirculate the overboard discharge water to a tank on the OWS suction side.
[4] This calibration generally takes place in a lab, but can be tested by use of a three-sample liquid aboard the vessel.
Coalescence is the breakdown of surface tension between oil droplets in an oil/water mixture which causes them to join and increase in size.
[8] This act gave rights to the surgeon general of the public health service to make programs to decrease the amount of pollution in the world's waters.
Electrochemical emulsification involves the generation of electrolytic bubbles that attract pollutants such as sludge and carry them to the top of the treatment chamber.
A carefully managed environment is needed for the microorganisms which includes nutrients and hydrocarbons such as oil or other contaminants, and oxygen.
In pilot scale studies, bio-remediation was used as one stage in a multi-stage purification process involving a plate separator to remove the majority of the contaminants and was able to treat pollutants at very low concentrations including organic contaminants such as glycerol, solvents, jet fuel, detergents, and phosphates.
Centrifugal oil-water separators are used for waste water processing and for cleanup of oil spills on sea or on lake.
Centrifugal oil-water separators are also used for filtering diesel and lubricating oils by removing the waste particles and impurity from them.
On a properly operated vessel only small amounts of bilge would be present as long as there are no equipment failures.
At the most basic level, the absolute absence of any type of standardization of OWS systems makes the initial investigation confusing, dirty, time-consuming and sometimes plain incorrect.
However, due to the criminal character of OWS violations the jointness concept is abandoned, which leads to very poor technical investigative methods and severe unnecessary disruptions to vessel operations.
In 2015, at the MAX1 Studies Conference held in Wilmington, North Carolina, maritime leaders from many different sectors gathered to discuss problems potential solutions regarding waste stream management.