Organization of the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) in the United States is a Bureau of the Department of the Interior with its headquarters located in Washington, D.C.
The resultant Restructuring Plan for the National Park Service built on earlier efforts within the Service – the 21st Century Task Force Report, the VAIL AGENDA, the NPS STRATEGIC PLAN, and the Recommendations of the Reorganization Work Group.
The plan reduced the number of central offices and by the creation of 16 ecological-cultural-geographical based clusters in seven regions.
Of the 16 ‘eco-clusters’ envisioned in the plan, only those clusters based on older regional offices, i.e., Boston, Seattle, and Santa Fe exist.
The National Park Service is the largest bureau in the department and has often required additional space.
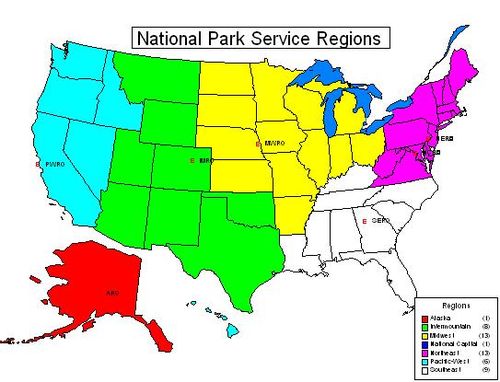
[2] The Northeast Region consisted of 73 parks in thirteen states – Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, New York, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Virginia.
A significant boundary adjustment on January 6, 1974 transferred to the Midwest Region the states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio and Wisconsin, and left the region with the states of Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia and West Virginia.
[2]: 79 The Intermountain Region consisted of parks in eight states: Montana, Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas.
[2]: 106 Rocky Mountain Region The Rocky Mountain Region consisted of 41 parks in seven states: Utah, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and a part of Arizona.
Boundary was adjusted on November 15, 1971 deleting most of Arizona and Utah and adding Arkansas and Louisiana.
[2]: 127 The Midwest Region consisted of 57 park units in thirteen states: Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Arkansas, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota, and North Dakota.
Originally created as Region two on August 1, 1937, it covered the Northern Rocky Mountains, Plains, and Western Great Lakes states.
[2]: 82 The Pacific-West Region consisted of parks in Washington, Oregon, California, Nevada, Idaho, and Hawaii, as well as the territories of Guam, Saipan, and American Samoa.
There were boundary changes in December 1969, when Alaska, Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Lava Beds NM were removed from the region and Lake Mead NRA was added.
[2]: 107 The Southeast Region consisted of 60 parks in nine states and two territories: Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, Louisiana, Alabama, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida, plus the Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico.