Oxytocin
[12][13] The adjective form is "oxytocic", which refers to medicines which stimulate uterine contractions, to speed up the process of childbirth.
[26] Further work on different synthetic routes for oxytocin, as well as the preparation of analogues of the hormone (e.g. 4-deamido-oxytocin) was performed in the following decade by Iphigenia Photaki.
[33] Oxytocin and vasopressin are the only known hormones released by the human posterior pituitary gland to act at a distance.
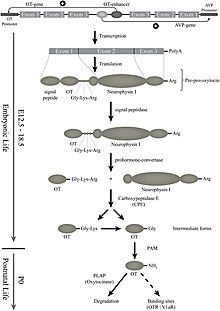
[37] The inactive precursor protein is progressively hydrolyzed into smaller fragments (one of which is neurophysin I) via a series of enzymes.
The last hydrolysis that releases the active oxytocin nonapeptide is catalyzed by peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM).
By chance, sodium ascorbate by itself was found to stimulate the production of oxytocin from ovarian tissue over a range of concentrations in a dose-dependent manner.
[43][44][45][46] In the hypothalamus, oxytocin is made in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei,[47] and is stored in Herring bodies at the axon terminals in the posterior pituitary.
These axons (likely, but dendrites have not been ruled out) have collaterals that innervate neurons in the nucleus accumbens, a brain structure where oxytocin receptors are expressed.
[49] Depending on the species, oxytocin receptor-expressing cells are located in other areas, including the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.
In the pituitary gland, oxytocin is packaged in large, dense-core vesicles, where it is bound to neurophysin I as shown in the inset of the figure; neurophysin is a large peptide fragment of the larger precursor protein molecule from which oxytocin is derived by enzymatic cleavage.
[58] The finding of significant amounts of this classically "neurohypophysial" hormone outside the central nervous system raises many questions regarding its possible importance in these diverse tissues.
The Leydig cells in some species have been shown to possess the biosynthetic machinery to manufacture testicular oxytocin de novo, to be specific, in rats (which can synthesize vitamin C endogenously), and in guinea pigs, which, like humans, require an exogenous source of vitamin C in their diets.
Furthermore, because the same regions of the brain are involved as in mammals, the study suggests oxytocin-based empathy may have evolved from a common ancestor many millions of years ago.
[48] Oxytocin receptors are expressed by neurons in many parts of the brain and spinal cord, including the amygdala, ventromedial hypothalamus, septum, nucleus accumbens, and brainstem, although the distribution differs markedly between species.
Further, oxytocin was correlated with participant desire to protect vulnerable in-group members, despite that individual's attachment to the conflict.
A study done in the Netherlands showed that oxytocin increased the in-group favoritism of their nation while decreasing acceptance of members of other ethnicities and foreigners.
[108] People also show more affection for their country's flag while remaining indifferent to other cultural objects when exposed to oxytocin.
Oxytocin is typically remembered for the effect it has on prosocial behaviors, such as its role in facilitating trust and attachment between individuals.
[120] Indeed, studies in rodents have shown oxytocin can efficiently inhibit fear responses by activating an inhibitory circuit within the amygdala.
Rats who are genetically modified to have a surplus of oxytocin receptors display a greater fear response to a previously conditioned stressor.
[130][131] A drug for sexual dysfunction, sildenafil enhances electrically evoked oxytocin release from the pituitary gland.
This phenomenon can be explained by looking at the role of gonadal hormones, specifically estrogen, which modulate the enhanced threat processing seen in females.
[136] Because oxytocin plays a role in social bonding, maternal behaviors and emotional connections between people, it is also informally referred to as the "love hormone".
Oxytocin is a peptide of nine amino acids (a nonapeptide) in the sequence cysteine-tyrosine-isoleucine-glutamine-asparagine-cysteine-proline-leucine-glycine-amide (Cys – Tyr – Ile – Gln – Asn – Cys – Pro – Leu – Gly – NH2, or CYIQNCPLG-NH2); its C-terminus has been converted to a primary amide and a disulfide bridge joins the cysteine moieties.
[167] Since this original Lee et al. paper, two other laboratories have confirmed Pro8-OT and documented additional oxytocin structural variants in this primate taxon.
Vargas-Pinilla et al. sequenced the coding regions of the OXT gene in other genera in new world primates and identified the following variants in addition to Leu8- and Pro8-OT: Ala8-OT, Thr8-OT, and Val3/Pro8-OT.
[169] Recent advances in analytical instrumental techniques highlighted the importance of liquid chromatography (LC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) for measuring oxytocin levels in various samples derived from biological sources.
[172] These important ion selections paved the way for the development of current methods of oxytocin quantification using MS instrumentation.