p-cycle protection
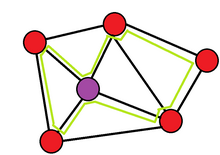
[3] In a mesh network, the spare capacity is used to create the ring like structures as shown in Figure 1.
Due to the nature of the rings assuming bi-directional line switched ring (BLSR), only 2 end nodes are involved in a case of a link failure to switch traffic to a pre-planned cycle (path) and recover, as it is demonstrated in Figure 2.
The types of p-cycles that are available are: Hamiltonian, Simple, Non-Simple, Span, Node encircling, Path, and Flow.
The Span, Node, Path, and Flow p-cycles are named after the type of protection offered to the network.
The p-cycles can be created after the working demands are routed in the network or at the same time depending on the needs and requirements.
[5] In the centralized method, the p-cycles can be determined and picked based on the possible candidate cycles from a large eligible set for the design in order to protect all the possible working channels and links.
[6] The Heuristic method presented called the ER-based unity-p-cycle, shows an attractive solution to solve the problem with creating p-cycles without the use of ILP.
This method is fast and simple to create a set of cycles, but suffers from inefficiency for the overall network design.
The distributed method for creating p-cycles differs from the centralized approach in a number of ways.
The distributed method deals with logical configuration and assignment of already in-place physical capacities.
[1] this means that the distributed method is aimed towards real life operations where the physical links are fixed but logical distinction can be made of how the spare and working capacity can be used and or decided.
Based on this idea, a number of statelets is sent throughout the network (broadcast) and forms a tree of states.
The other role is the Tandem, which works by mediating the state broadcasts competition with new rules and criteria not found in Selfhealing networks.
The Tandem role also dictates allowed discovery of p-cycles by the Cycler node type.
Based on the DCPC, the p-cycles are self-organized in the spare capacity of the network and are found in a distributed way.
The algorithm can be re-run each time a network change occurs to create an optimum use of spare capacity.
The aggregation of the messages left or generated by those ants is the basis of forming p-cycles in the system.
showed that an efficient way to create p-cycles can be achieved in mesh networks that are flat.
In this type of network the ability of the p-cycle to protect more than one straddling span allowed it to reach an efficiency of