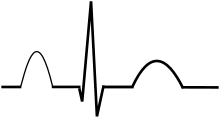
P wave (electrocardiography)
The depolarization front is carried through the atria along semi-specialized conduction pathways including Bachmann's bundle resulting in uniform shaped waves.
Depolarization originating elsewhere in the atria (atrial ectopics) result in P waves with a different morphology from normal.
[7] This appears particularly commonly in exacerbations of chronic obstructive lung disease.
[8] If the baseline has a totally irregular form, this suggests fibrillatory waves of atrial fibrillation or possibly artefact; a saw tooth shaped baseline suggests the flutter waves of atrial flutter.
The clinical relevance of this is that, although a normal phenomenon, the nadir of the Ta wave can occur just after the QRS complex and cause ST depression similar to (and easily mistaken with) that occurring with disease states such as cardiac ischaemia.