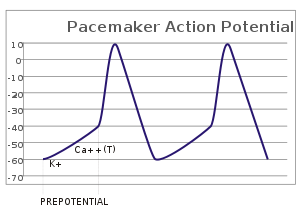
Pacemaker potential
It employs pacemaker cells that generate electrical impulses, known as cardiac action potentials.
[2] In a healthy sinoatrial node (SAN, a complex tissue within the right atrium containing pacemaker cells that normally determine the intrinsic firing rate for the entire heart[3][4]), the pacemaker potential is the main determinant of the heart rate.
Evidence in support of the active presence of K+, Ca2+, Na+ channels and Na+/K+ exchanger during the pacemaker phase have been variously reported in the literature, but several indications point to the “funny”(If) current as one of the most important.
There is now substantial evidence that also sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+-transients participate to the generation of the diastolic depolarization via a process involving the Na–Ca exchanger.
[7] This depolarization is caused by very small net inward currents of calcium ions across the cell membrane, which gives rise to the action potential.
[8][9] Bio-pacemakers are the outcome of a rapidly emerging field of research into a replacement for the electronic pacemaker.