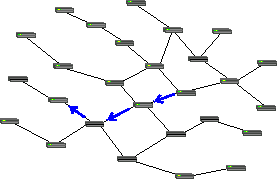
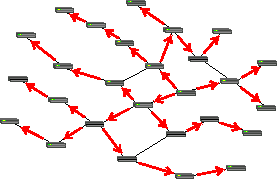
Packet forwarding
Less common than broadcasting, but perhaps of greater utility and theoretical significance, is multicasting, where a packet is selectively duplicated and copies delivered to each of a set of recipients.
However, as illustrated in the diagrams, nodes can forward packets to create multicast or broadcast distributions from naturally unicast media.
At nodes where multiple outgoing links are available, the choice of which, all, or any to use for forwarding a given packet requires a decision-making process that, while simple in concept, is sometimes bewilderingly complex.
Since a forwarding decision must be made for every packet handled by a node, the total time required for this can become a major limiting factor in overall network performance.
Much of the design effort of high-speed routers and switches has been focused on making rapid forwarding decisions for large numbers of packets.