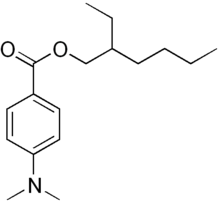
Padimate O
This yellowish water-insoluble oily liquid is an ester formed by the condensation of 2-ethylhexanol with dimethylaminobenzoic acid.
Padimate O absorbs ultraviolet rays, thereby preventing direct DNA damage by UV-B.
An in vitro yeast study conducted in 1993 demonstrated the sunlight-induced mutagenicity of padimate O.
[1] The photobiological properties of padimate O resemble those of Michler's ketone, which is considered photocarcinogenic in rats and mice.
[2] However, multiple in vivo studies conducted in hairless mice following topical application of padimate O have demonstrated no carcinogenic effects and that padimate O reduces the number of and delays the appearance of UV-induced skin tumors.