Peptide vaccine
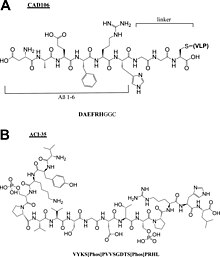
The peptides mimic the epitopes of the antigen that triggers direct or potent immune responses.
[1] Peptide vaccines can not only induce protection against infectious pathogens and non-infectious diseases but also be utilized as therapeutic cancer vaccines, where peptides from tumor-associated antigens are used to induce an effective anti-tumor T-cell response.
The third generation of vaccines is the DNA or plasmid that can express the proteins of the pathogen.
[4] Advantages: Disadvantages: The whole peptide vaccine is to mimic the epitope of an antigen, so epitope design is the most important stage of vaccine development and requires an accurate understanding of the amino acid sequence of the immunogenic protein interested.
The designed epitope is expected to generate strong and long-period immuno-response against the pathogen.