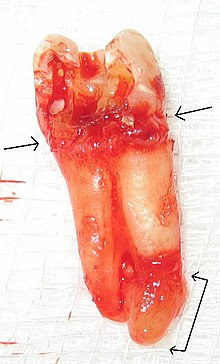
Dental abscess
The main types of dental abscess are: The pain is continuous and may be described as extreme, growing, sharp, shooting, or throbbing.
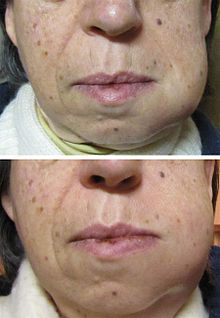
In some cases, a tooth abscess may perforate bone and start draining into the surrounding tissues creating local facial swelling.
[2] If left untreated, a severe tooth abscess may become large enough to perforate bone and extend into the soft tissue eventually becoming osteomyelitis and cellulitis respectively.
Severe complications requiring immediate hospitalization include Ludwig's angina, which is a combination of growing infection and cellulitis which closes the airway space causing suffocation in extreme cases.
Also infection can spread down the tissue spaces to the mediastinum, causing significant consequences on the vital organs such as the heart.
Depending on the severity of the infection, the sufferer may feel only mildly ill, or may in extreme cases require hospital care.
There is no clear evidence to rule out if patients with acute dental abscesses can benefit from systemic antibiotic prescriptions.