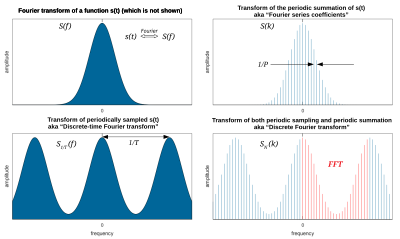
Periodic summation
with period P by summing the translations of the function
by integer multiples of P. This is called periodic summation:
[1][2] That identity is a form of the Poisson summation formula.
Similarly, a Fourier series whose coefficients are samples of
at constant intervals (T) is equivalent to a periodic summation of
Likewise, the periodic summation of an integrable function is its convolution with the Dirac comb.
If a periodic function is instead represented using the quotient space domain
are equivalence classes of real numbers that share the same fractional part when divided by