Plant stem
It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, engages in photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue.
respiration, photosynthesis, transport, storage) as well as acting as structural support and forming new meristems.
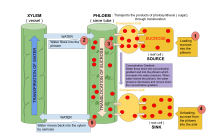
Vascular tissue, consisting of xylem, phloem and cambium; provides long distance transport of water, minerals and metabolites (sugars, amino acids); whilst aiding structural support and growth.
The epidermis also may contain stomata for gas exchange and multicellular stem hairs called trichomes.
Areas of loosely packed cells in the periderm that function in gas exchange are called lenticels.
The seasonal variation in growth from the vascular cambium is what creates yearly tree rings in temperate climates.
The dead, usually darker inner wood of a large diameter trunk is termed the heartwood and is the result of tylosis.
Monocots rarely produce secondary growth and are therefore seldom woody, with palms and bamboo being notable exceptions.
In cross section, the vascular tissue does not form a complete cylinder where a leaf gap occurs.
Foreign chemicals such as air pollutants,[9] herbicides and pesticides can damage stem structures.
Vegetables from stems are asparagus, bamboo shoots, cactus pads or nopalitos, kohlrabi, and water chestnut.
Gum arabic is an important food additive obtained from the trunks of Acacia senegal trees.
Wood is used in thousands of ways; it can be used to create buildings, furniture, boats, airplanes, wagons, car parts, musical instruments, sports equipment, railroad ties, utility poles, fence posts, pilings, toothpicks, matches, plywood, coffins, shingles, barrel staves, toys, tool handles, picture frames, veneer, charcoal and firewood.
Bamboo stems also have hundreds of uses, including in paper, buildings, furniture, boats, musical instruments, fishing poles, water pipes, plant stakes, and scaffolding.
Bast fibers for textiles and rope are obtained from stems of plants like flax, hemp, jute and ramie.
Amber is fossilized sap from tree trunks; it is used for jewelry and may contain preserved animals.