Plasmonic nanolithography
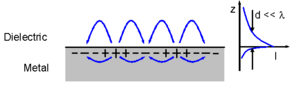
Nevertheless, the excitation of SPPs necessitate momentum mismatch; prism and grating coupling methods are common.
[1] Planar lens imaging nanolithography uses plasmonic lenses or negative-index superlenses, which were first proposed by John Pendry.
[12] Kim et al. has developed a ~50 nm resolution scanning probe with a patterning speed of ~10 mm/s.
[6][15][16] Lin et al. also used localized thermal excitations in gold nanoparticles to fabricate two-dimensional structures such as patterned graphene and molybdenum disulfide monolayers in a process termed as "optothermoplasmonic nanolithography.
"[17] Photochemical effects of LSP resonances were also used as a catalyst in lithographic processes:[18] Saito et al. demonstrated selective etching of silver nanocubes on titanium dioxide substrates by the means of plasmon-induced charge separation.